Publications
2025
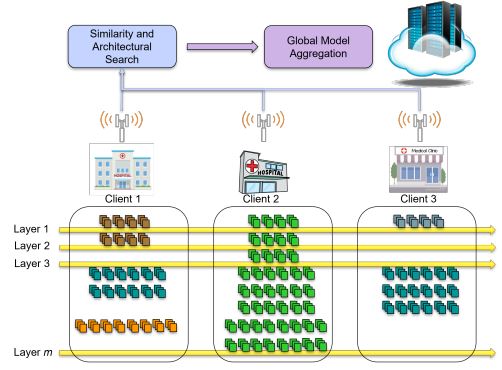
- FLEXFL: Flexible Federated Learning for Customized Network Architectures in 6GSunder Ali Khowaja, Ik Hyun Lee, Parus Khuwaja, and 3 more authorsIn IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2025
With the continuous and fast-changing land-scape in communication networks and artificial intelligence (AI), the researchers are interested in expedited standardization and realization of 6G networks. Federated learning (FL) is one of the paradigms that allows the 6G networks to support a diverse range of devices. Very few studies address the problem of flexibility and heterogeneity for AI network architectures in FL paradigm, that could be a potential key changer for standardization and realization of 6G networks. However, they either consider width-only or depth-only to provide flexibility support. Furthermore, the existing studies do not address the problem of weight scale variation while performing the global model aggregation at the server side. In this regard, we propose flexible federated learning (FLEXFL) for the support of heterogeneous AI network architectures in 6G communication systems. The proposed network not only considers the width but also the depth of the network architecture to make it compliant with the global model aggregation. We also address weight scale variation (WSV) while updating the global model with weight normalization, which is one of the problems associated with existing studies. We perform experimental analysis on two publicly available datasets and a few network architectures to show the efficacy of the proposed approach. The results reveal that the FLEXFL outperforms existing state-of-the-art works in both the IID and non-IID settings, accordingly.
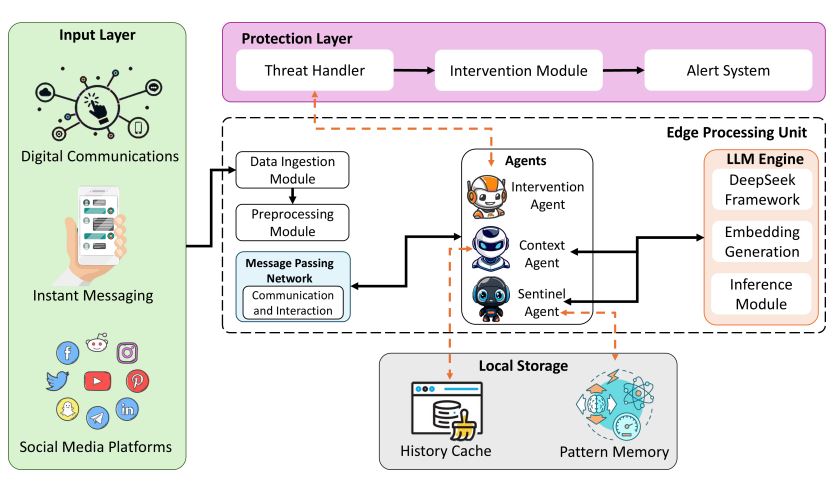
@inproceedings{FlexFL, title = {FLEXFL: Flexible Federated Learning for Customized Network Architectures in 6G}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, Ik Hyun and Khuwaja, Parus and Bhatti, Naveed Anwar and Singh, Keshav and Dev, Kapal}, booktitle = {IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference (WCNC)}, pages = {1-6}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/WCNC61545.2025.10978249}, dimensions = {true}, } - EdgeAIGuard: Agentic LLMs for Minor Protection in Digital SpacesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and Kapal DevIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025
Social media has become integral to minors’ daily lives and is used for various purposes, such as making friends, exploring shared interests, and engaging in educational activities. However, the increase in screen time has also led to heightened challenges, including cyberbullying, online grooming, and exploitations posed by malicious actors. Traditional content moderation techniques have proven ineffective against exploiters’ evolving tactics. To address these growing challenges, we propose the EdgeAIGuard content moderation approach that is designed to protect minors from online grooming and various forms of digital exploitation. The proposed method comprises a multi-agent architecture deployed strategically at the network edge to enable rapid detection with low latency and prevent harmful content targeting minors. The experimental results show the proposed method is significantly more effective than the existing approaches.
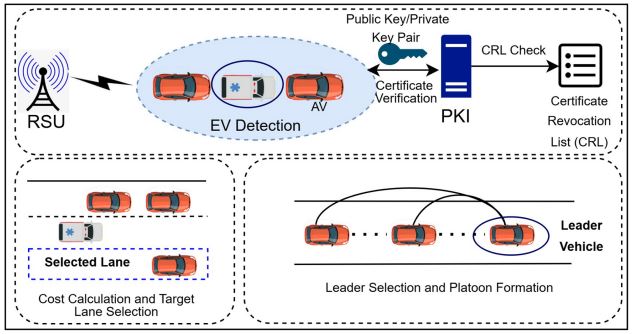
@article{EdgeAIGuard, title = {EdgeAIGuard: Agentic LLMs for Minor Protection in Digital Spaces}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, volume = {Early Access}, pages = {1-10}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2025.3574961}, dimensions = {true}, } - Emergency Vehicle Navigation in Connected Autonomous Systems Using Enhanced Traffic Management SystemGunasekaran Raja, Sudha Anbalagan, Sugeerthi Gurumoorthy, and 5 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025
Autonomous vehicle (AV) usage has become predominant in the rapidly evolving landscape of urban transportation. Integrating AVs and non-AVs in the existing traffic infrastructure has significantly increased the complexity of traffic patterns. This research work primes the enhanced Traffic Management System (e-TMS), a solution implemented to expedite emergency vehicle (EV) travel in the context of connected AVs (CAVs) and ensured secured communication employing public key infrastructure (PKI) among the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) framework. When an EV is detected, the IoV system verifies the EV’s signal using PKI, ensuring its authenticity and integrity by encrypting the communication between the EV and road side units (RSUs). Further, the e-TMS activates the platooning process where CAVs in the EV’s lane shift to the adjacent lanes and dynamically form platoons to create a dedicated lane for the EV. To further optimize the platooning process, an adaptive smart leader selection (ASLS) algorithm is employed to select a leader vehicle spontaneously among the AVs based on the proximity to the EV, communication reliability, and lane position. Radio Detection and Ranging devices aid this platooning process by providing distance and target velocity, which are needed to maintain the required distance between the AVs and ensure safe platoon formation. The e-TMS enhances EV response times and overall traffic flow efficiency and resulted in 27.8% increase in mean speed compared to the traditional methods.
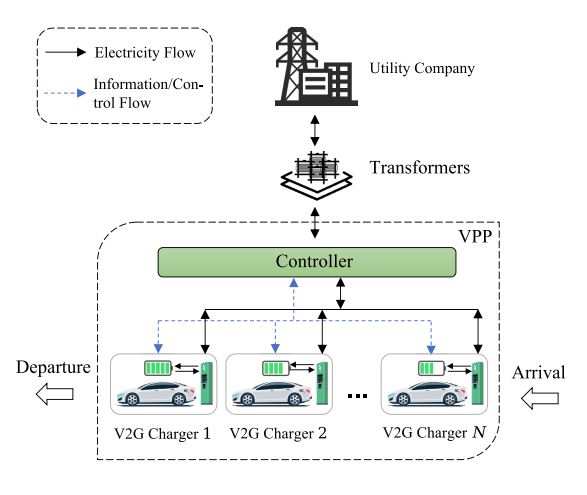
@article{VNavigation, title = {Emergency Vehicle Navigation in Connected Autonomous Systems Using Enhanced Traffic Management System}, author = {Raja, Gunasekaran and Anbalagan, Sudha and Gurumoorthy, Sugeerthi and Jegathesan, Darshini and Girivel, Niveditha Subramanian and Sundaram, Varsha Mani Shanmuga and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, volume = {12}, pages = {20670-20677}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2025.3545424}, dimensions = {true}, } - Cost-Efficient Power Orchestration in Electric Vehicle-Integrated VPP Using Lightweight Multi-Agent Reinforcement LearningDongyu Zheng, Lei Liu, Guoming Tang, and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025
Virtual power plants (VPPs) have emerged as an advanced solution for coordinating distributed energy resources (DERs), including the stored energy of electric vehicles (EVs). The substantial demand for EV charging imposes significant stress on the electrical grid, resulting in elevated energy costs for operators. On the other hand, the advent of reversible charging technologies offers a promising method to harness the surplus energy from EVs that do not require immediate charging. In this study, we introduce the concept of EV-integrated VPP in place of the traditional charging station. By designing a tailored mathematical model, we optimize the charging and discharging schedule, termed optimal power orchestration, which aims to minimize the energy costs as well as EV battery degradation. We further design a lightweight multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) based approach to tackle the optimal power orchestration problem by reformulating it as a decentralized partially observable Markov decision process (Dec-POMDP). Meanwhile, knowledge distillation is also incorporated into the proposed method to enable efficient deployment in such a distributed resource-constrained environment. Through extensive experiments utilizing real-world EV charging data and realistic scenario settings, our findings demonstrate significant reductions in energy costs and battery degradation by 15.5% and 71.1%, respectively, compared to the baseline method.
@article{VPPRL, title = {Cost-Efficient Power Orchestration in Electric Vehicle-Integrated VPP Using Lightweight Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning}, author = {Zheng, Dongyu and Liu, Lei and Tang, Guoming and Guo, Deke and Hu, Jia and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, volume = {Early Access}, pages = {1-13}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TITS.2025.3577438}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 AiCareGaitRehabilitation: Multi-modalities sensor data fusion for AI-IoT enabled realtime electrical stimulation device for pre-Fog and post-Fog to person with Parkinson’s DiseaseHemant Ghayvat, Muhammad Awais, Rebakah Geddam, and 3 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2025
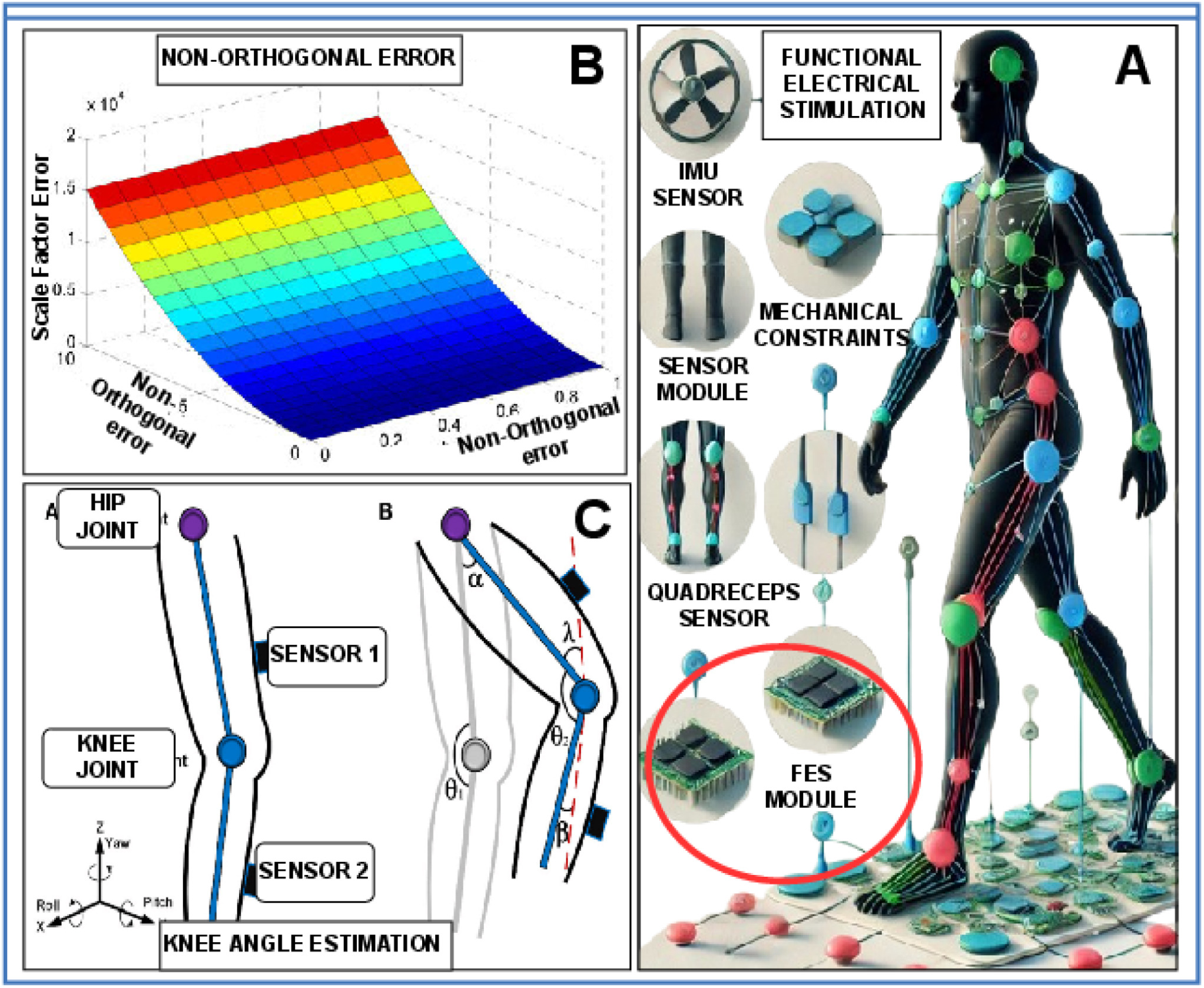
AiCareGaitRehabilitation: Multi-modalities sensor data fusion for AI-IoT enabled realtime electrical stimulation device for pre-Fog and post-Fog to person with Parkinson’s DiseaseHemant Ghayvat, Muhammad Awais, Rebakah Geddam, and 3 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2025The neuromuscular dysfunction known as Freezing of Gait (FoG), which is more prevalent in individuals suffering from Parkinson’s Disease (PD), significantly reduces the quality of life and increases their risk of falling. Wearable FoG sensing technologies provide timely biofeedback cues to assist people regain control over their gait. However, the devices being bulky, intrusive, and annoyance of current FoG detection algorithms limit their usability in real-world applications. This study proposes a more efficient approach by integrating the FoG detection fusion algorithm into a Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) module. The design leverages features with low computational requirements and specialized hardware to minimize the use of physical space and memory. The Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) approach with SVM output was deployed to classify FoG and non-FoG periods in real-time. Additionally, the study uses CNN algorithms in fusion with data from a triaxial accelerometer, strain sensors, and piezoelectric plantar sensors to test shank-worn FoG detection devices. The study demonstrates that electrical stimulation-based cueing strategies significantly improve gait control and mitigate FoG episodes in people with Parkinson’s disease. The AiCareGaitRehabilitation system employs a multi-modal sensor fusion strategy to improve the efficacy of the FES device. Data from various sensors—such as strain sensor, 18 plantar sensors, and four quadriceps sensors—the system provides a holistic view of both pre-freezing of Gait (pre-FOG) and post-freezing of Gait (post-FOG) scenarios. This research aims to improve mobility, reduce fall risks, and eventually improve the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
@article{AiCareGait, title = {AiCareGaitRehabilitation: Multi-modalities sensor data fusion for AI-IoT enabled realtime electrical stimulation device for pre-Fog and post-Fog to person with Parkinson’s Disease}, author = {Ghayvat, Hemant and Awais, Muhammad and Geddam, Rebakah and Quasim, Mohammad Tabrez and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {Information Fusion}, volume = {122}, pages = {103155}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.inffus.2025.103155}, dimensions = {true}, } - Federated Learning in STAR-RIS Aided SAGINsWu Min, Kefeng Guo, Kapal Dev, and 4 more authorsIEEE Communication Standard Magazine, 2025
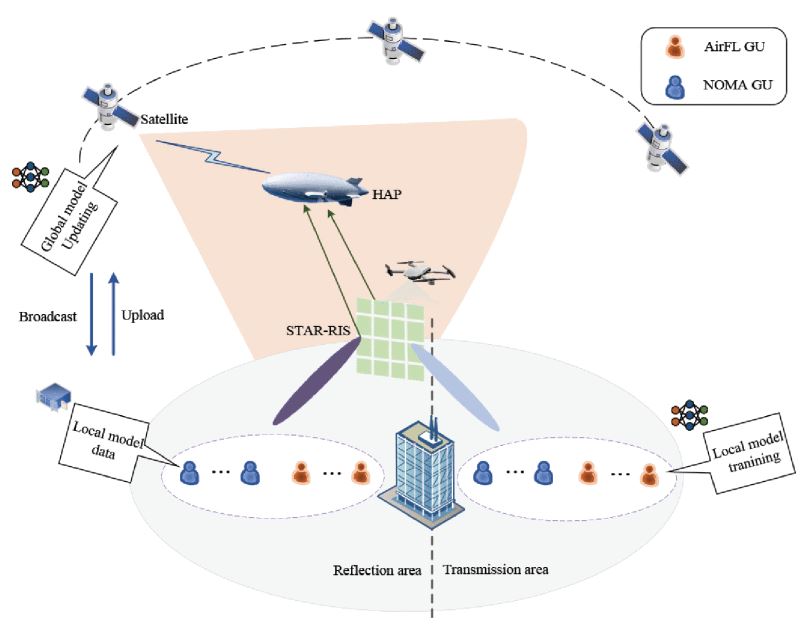
Satellite-aerial-ground integrated network (SAGIN) is considered to be an advanced architecture that offers seamless coverage, flexible access, and efficient connectivity. However, several challenges emerge during the construction of SAGINs, which include complex propagation environments and limited spectrum resources. The aforementioned challenges can be addressed in a cost-effective manner by integrating simultaneous transmission and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RISs). The STAR-RISs are capable of reflecting and transmitting the incident signals passively in order to serve users on both sides of the panel. Given the self-organizing nature of STAR-RIS-aided SAGINs, meticulous resource allocation and transmission strategy adaptation are imperative to accommodate changes in multiple communication node environments. Recently, federated learning has been envisioned as a pioneering distributed machine learning (ML) approach for managing the multi-objective optimization problem in STAR-RIS-aided SAGINs. This approach strives to balance the trade-offs between wireless communication performance and model efficiency. In this work, we present the advantages and potential directions for employing federated learning in STAR-RIS-aided SAGINs through multi-objectives optimization. Furthermore, to illustrate the practical application of federated learning in STAR-RIS-aided SAGINs, we present two case studies utilizing federated deep reinforcement learning, based on the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) scheme.
@article{SAGIN2025, title = {Federated Learning in STAR-RIS Aided SAGINs}, author = {Min, Wu and Guo, Kefeng and Dev, Kapal and Hamadi, Hussam Al and Singh, Keshav and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Li, Xingwang}, journal = {IEEE Communication Standard Magazine}, volume = {9}, pages = {23-29}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MCOMSTD.2025.3569008}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Block Encryption LAyer (BELA): Zero-Trust Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks for Federated Learning in 5G/6G SystemsSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 4 more authorsIEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2025
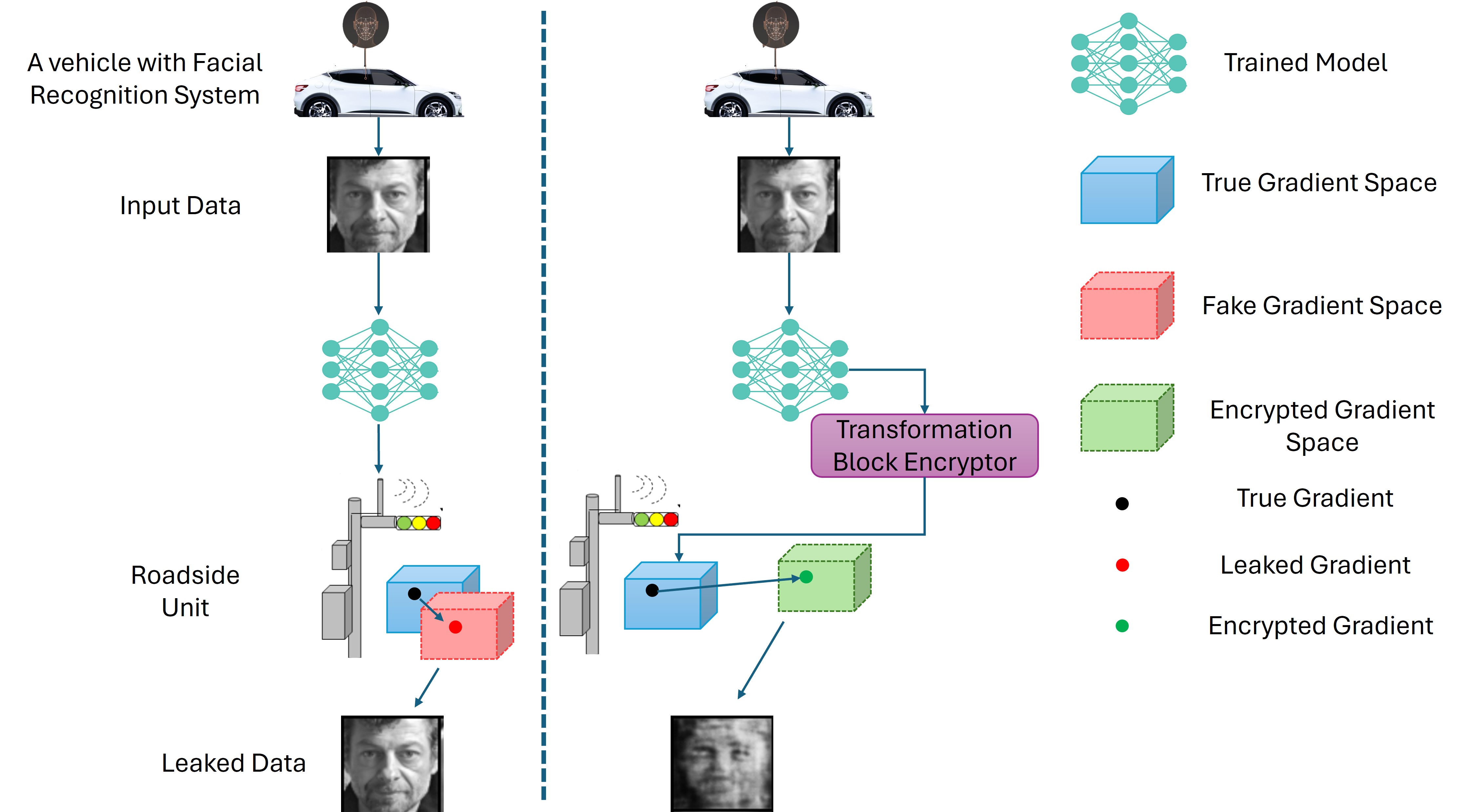
Block Encryption LAyer (BELA): Zero-Trust Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks for Federated Learning in 5G/6G SystemsSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 4 more authorsIEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2025Federated Learning (FL) paradigm has been very popular in the implementation of 5G and beyond communication systems as it provides necessary security for the users in terms of data. However, the FL paradigm is still vulnerable to model inversion attacks, which allow malicious attackers to reconstruct data by using the trained model gradients. Such attacks can be carried out using generative adversarial networks (GANs), generative models, or by backtracking the model gradients. A zero-trust mechanism involves securing access and interactions with model gradients under the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This proactive approach ensures that sensitive information, such as model gradients, is kept private, making it difficult for adversaries to infer the private details of the users. This paper proposes a zero-trust based Block Encryption LAyer (BELA) module that provides defense against the model inversion attacks in FL settings. The BELA module mimics the Batch normalization (BN) layer in the deep neural network architecture that considers the random sequence. The sequence and the parameters are private to each client, which helps in providing defense against the model inversion attacks. We also provide extensive theoretical analysis to show that the proposed module is integratable in a variety of deep neural network architectures. Our experimental analysis on four publicly available datasets and various network architectures show that the BELA module can increase the mean square error (MSE) up to 194% when a reconstruction attempt is performed by an adversary using existing state-of-the-art methods
@article{BELA2025, title = {Block Encryption LAyer (BELA): Zero-Trust Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks for Federated Learning in 5G/6G Systems}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Singh, Keshav and Li, Xingwang and Nikolaos, Bartzoudis and Comsa, Ciprian R}, journal = {IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society}, volume = {6}, pages = {807-819}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/OJCOMS.2025.3526768}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Image Registration and Deep NeuroFuzzy Networks for Mitigating Atmospheric Turbulence Effects in Consumer-Based Optical ImagingSunder Ali Khowaja, Usman Ali, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2025
Image Registration and Deep NeuroFuzzy Networks for Mitigating Atmospheric Turbulence Effects in Consumer-Based Optical ImagingSunder Ali Khowaja, Usman Ali, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2025Consumer-based optical imaging systems are characterized as big data processing systems, which are drastically affected by atmospheric turbulences that add geometric distortions and blur effect to the images when used in outdoor condition. Physics-grounded simulators have been proposed recently to generate synthetic data but the generalization to the real-world turbulent images is not so good. In this paper, we combine the characteristics of image registration, deep neurofuzzy methods, and channel-attention based discriminative learning strategy to propose image registration, neurofuzzy based denoising, and deblurring network (RND2Net). The RND2Net is designed on a principle that it does not require turbulent image pairs (ground truth images) to train the network, which closely resembles the real-world situation used as consumer devices. The registration module focuses on the region-based fusion techniques while the denoising and deblurring module incorporates deep neurofuzzy network along with dense residual blocks and channel attention mechanism to train the network. The RND2Net is also designed to reduce the noise and blur effect from images, while generalizing on the down-stream tasks, such as text recognition. Experimental results show that the RND2Net yields better performance quantitatively as qualitatively on synthetic and real-world datasets in comparison to existing state-of-the-art methods
@article{turb2025, title = {Image Registration and Deep NeuroFuzzy Networks for Mitigating Atmospheric Turbulence Effects in Consumer-Based Optical Imaging}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Ali, Usman and Dev, Kapal and Lee, Ik Hyun}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics}, volume = {}, pages = {}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TCE.2025.3528544}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 SelfFed: Self-supervised federated learning for data heterogeneity and label scarcity in medical imagesSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Syed Muhammad Anwar, and 1 more authorExpert Systems With Applications, 2025
SelfFed: Self-supervised federated learning for data heterogeneity and label scarcity in medical imagesSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Syed Muhammad Anwar, and 1 more authorExpert Systems With Applications, 2025Self-supervised learning in the federated learning paradigm has been gaining a lot of interest both in industry and research due to the collaborative learning capability on unlabeled yet isolated data. However, self-supervised based federated learning strategies suffer from performance degradation due to label scarcity and diverse data distributions, i.e., data heterogeneity. In this paper, we propose the SelfFed framework for medical images to overcome data heterogeneity and label scarcity issues. The first phase of the SelfFed framework helps to overcome the data heterogeneity issue by leveraging the pre-training paradigm that performs augmentative modeling using Swin Transformer-based encoder in a decentralized manner. The label scarcity issue is addressed by fine-tuning paradigm that introduces a contrastive network and a novel aggregation strategy. We perform our experimental analysis on publicly available medical imaging datasets to show that SelfFed performs better when compared to existing baselines and works. Our method achieves a maximum improvement of 8.8% and 4.1% on Retina and COVID-FL datasets on non-IID datasets. Further, our proposed method outperforms existing baselines even when trained on a few (10%) labeled instances.
@article{selffed2024, title = {SelfFed: Self-supervised federated learning for data heterogeneity and label scarcity in medical images}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Anwar, Syed Muhammad and Linguraru, Marius George}, journal = {Expert Systems With Applications}, volume = {261}, pages = {125493}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125493}, dimensions = {true}, }
2024
-
 RSMA-assisted SHAPTINs: secrecy performance under imperfect hardware and channel estimation errorsZhou Feng, Kefeng Guo, Cheng Jian, and 4 more authorsNeural Computing and Applications, 2024
RSMA-assisted SHAPTINs: secrecy performance under imperfect hardware and channel estimation errorsZhou Feng, Kefeng Guo, Cheng Jian, and 4 more authorsNeural Computing and Applications, 2024Satellite high aerial platform terrestrial integrated networks have become the hot topic these years, which have been regarded as the major part of the intelligence of things for future networks. During this work, we investigate the secrecy performance for rate-splitting multiple access-assisted satellite high aerial platform terrestrial integrated networks. Besides, imperfect hardware and channel estimation errors are considered in the secrecy networks. Moreover, to enhance the energy utilization efficiency, rate-splitting multiple access scheme is utilized into the considered network, which is prior to that of the non-orthogonal multiple access scheme. What’s more, to enhance the satellite transmission, multiple high aerial platforms are used to forward the transmission along with multiple eavesdroppers. In addition, the direct transmission link is not considered in the secrecy networks due to the heavy fading and obstacles. Relied on the former considerations, the exact and asymptotic analysis for the secrecy performance is further obtained to confirm the rightness of the analysis. Finally, some representative Monte Carlo simulations are carried out to validate the obtained results.
@article{RSMA2024, title = {RSMA-assisted SHAPTINs: secrecy performance under imperfect hardware and channel estimation errors}, author = {Feng, Zhou and Guo, Kefeng and Jian, Cheng and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Gadekallu, Thippa Reddy and Hamadi, Hussam Al}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, volume = {}, pages = {}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-024-10526-2}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Depression Detection From Social Media Posts Using Emotion Aware Encoders and Fuzzy Based Contrastive NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Parus Khuwaja, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024
Depression Detection From Social Media Posts Using Emotion Aware Encoders and Fuzzy Based Contrastive NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Parus Khuwaja, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024Post COVID-19 and recent advancement in terms of language models, researchers have shown a lot of interest in analyzing social media posts for analyzing mental state of the users. Social media platforms are the epitome of sharing individual thoughts and feelings through textual posts and linguistic cues. Therefore, the textual modality from social media posts can be leveraged for detecting early signs of stress, depression or other mental health conditions, accordingly. Existing methods mainly focus on the feature engineering, shallow learning, and employing of deep learning architectures to improve the mental state recognition performance. Seldom the study uses an established knowledge-base that is available to model mentalization and emotional aspect to improving the depression and stress recognition. In this regard, we propose emotion aware contrastive networks (EAC-net) that leverages the existing knowledge-base and propose some new ones to model the emotional and mentalization aspect in order to improve the recognition of stress and depression state from textual posts. Furthermore, we propose a feature-level fusion and weighting mechanism using GRUs and self-attention layers to weight and select the important features. Lastly, the EAC-Net uses a supervised contrastive learning strategy to train the network. The proposed method is evaluated on four publicly available datasets. Experimental results reveal that the EAC-Net achieves state-of-the-art results by outperforming baselines and existing methods by atleast 1.86%, 0.72%, 3.43%, and 3.64% on four publicly available datasets using F1-measure as the evaluation metric.
@article{EACNet2024, title = {Depression Detection From Social Media Posts Using Emotion Aware Encoders and Fuzzy Based Contrastive Networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Nkenyereye, Lewis and Khuwaja, Parus and Hamadi, Hussam Al and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems}, volume = {Early Access}, pages = {1-11}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3461776}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Safeguarding Medical AI: Insights and Addressing Adversarial Threats in Consumer ElectronicsBraj Kishore Jha, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 2024
Safeguarding Medical AI: Insights and Addressing Adversarial Threats in Consumer ElectronicsBraj Kishore Jha, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 2024The unprecedented success of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in the medical field has revolutionized healthcare systems across the globe. As a powerful computer vision and image processing tool, AI has leveraged early and accurate diagnosis of diseases facilitating early interventions of medical professionals. The Consumer Electronics (CE) in the medical arena range from smart wearable devices to sophisticated tools, that monitor medical signals such as Electroencephalogram (EEG) and electrocardiogram (ECG), and capture radiographic images such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that act as biomarkers for medical analysis. However, with its emergence, an associated problem has also surfaced in the form of its vulnerability to adversarial attacks. This work highlights different ways in which undetectable adversarial attacks pose a threat to the medical CE ecosystem. We simultaneously explore methods to mitigate the vulnerability of our medical domain against such attacks.
@article{SafeMedicalAI, title = {Safeguarding Medical AI: Insights and Addressing Adversarial Threats in Consumer Electronics}, author = {Jha, Braj Kishore and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Pandey, Ankur}, journal = {IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine}, doi = {10.1109/MCE.2024.3443543}, volume = {Early Access}, pages = {1-6}, year = {2024}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Blind Enhancement of Compressed Image: Methods and ResultsRen Yang, Radu Timofte, Bingchen Li, and 52 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2024
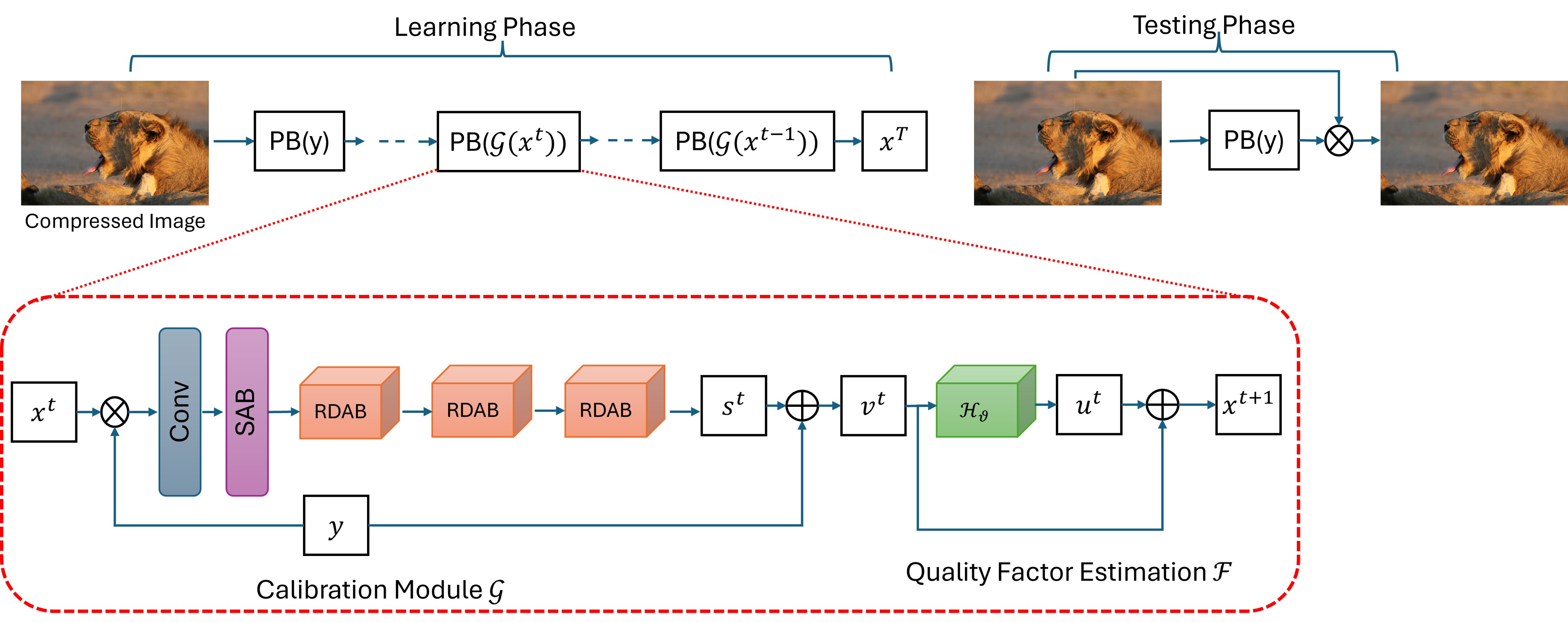
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Blind Enhancement of Compressed Image: Methods and ResultsRen Yang, Radu Timofte, Bingchen Li, and 52 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2024This paper reviews the Challenge on Blind Enhancement of Compressed Image at NTIRE 2024, which aims at enhancing the quality of JPEG images which are compressed with unknown quality factor. The challenge requires that the total size of codes and pre-trained model(s) cannot exceed 300 MB, since we encourage solutions for blind enhancement with generalized models, instead of separately training several models for each quality factor. In this report, we summarize the detailed settings of the challenge, the final results, and the solutions proposed by the participants. The challenge has 129 registered participants and received 13 valid submissions. Several teams (including all TOP 3 teams) have publicly released the codes (see Sec. 4). They gauge the state-of-the-art of blind quality enhancement of compressed image.
@inproceedings{NTIRE2024, title = {NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Blind Enhancement of Compressed Image: Methods and Results}, author = {Yang, Ren and Timofte, Radu and Li, Bingchen and Li, Xin and Guo, Mengxi and Zhao, Shijie and Zhang, Li and Chen, Zhibo and Zhang, Dongyang and Arora, Yash and Arora, Aditya and Chen, Yuanbin and Tang, Hui and Wang, Tao and Zhao, Longxuan and Chen, Bin and Tong, Tong and Mo, Qiao and Bao, Jingwei and Hao, Jinhua and Ding, Yukang and Li, Hantang and Sun, Ming and Zhou, Chao and Zhu, Shuyuan and Jin, Zhi and Wang, Wei and Zhan, Dandan and Wu, Jiawei and Wu, Jiahao and Tu, Luwei and An, Hongyu and Zhang, Xinfeng and Yeo, Woon-Ha and Oh, Wang-Taek and Kim, Young-Il and Ryu, Han-Cheol and Sun, Long and Zhen, Mingjun and Pan, Jinshan and Dong, Jiangxin and Tang, Jinhui and Du, Yapeng and Li, Ao and He, Ziyang and Luo, Lei and Zhu, Ce and Yao, Xin and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, IK Hyun and Lee, Jaeho and Kim, Seongwan and A, Sharif S M and Khujaev, Nodirkhuja and Tsoy, Roman}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)}, pages = {6524-6535}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/CVPRW63382.2024.00652}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 ChatGPT Needs SPADE (Sustainability, PrivAcy, Digital divide, and Ethics) Evaluation: A ReviewSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsCognitive Computation, 2024
ChatGPT Needs SPADE (Sustainability, PrivAcy, Digital divide, and Ethics) Evaluation: A ReviewSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsCognitive Computation, 2024ChatGPT is another large language model (LLM) vastly available for the consumers on their devices but due to its performance and ability to converse effectively, it has gained a huge popularity amongst research as well as industrial community. Recently, many studies have been published to show the effectiveness, efficiency, integration, and sentiments of chatGPT and other LLMs. In contrast, this study focuses on the important aspects that are mostly overlooked, i.e. sustainability, privacy, digital divide, and ethics and suggests that not only chatGPT but every subsequent entry in the category of conversational bots should undergo Sustainability, PrivAcy, Digital divide, and Ethics (SPADE) evaluation. This paper discusses in detail the issues and concerns raised over chatGPT in line with aforementioned characteristics. We also discuss the recent EU AI Act briefly in accordance with the SPADE evaluation. We support our hypothesis by some preliminary data collection and visualizations along with hypothesized facts. We also suggest mitigations and recommendations for each of the concerns. Furthermore, we also suggest some policies and recommendations for EU AI policy act concerning ethics, digital divide, and sustainability.
@article{SPADE, title = {ChatGPT Needs SPADE (Sustainability, PrivAcy, Digital divide, and Ethics) Evaluation: A Review}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Wang, Weizheng and Nkenyereye, Lewis}, journal = {Cognitive Computation}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s12559-024-10285-1}, volume = {16}, pages = {2528-2550}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 RIS-Empowered Satellite-Aerial-Terrestrial Networks With PD-NOMARui Liu, Kefeng Guo, Xingwang Li, and 4 more authorsIEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024
RIS-Empowered Satellite-Aerial-Terrestrial Networks With PD-NOMARui Liu, Kefeng Guo, Xingwang Li, and 4 more authorsIEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024Satellite-aerial-terrestrial network (SATN) is considered as a promising architecture for sixth-generation (6G) wireless communication networks to achieve seamless coverage, flexible wireless access, and high data rate. Moreover, non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA), and reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) can significantly increase spectrum and energy efficiency. Recently, the integration of these two technologies and SATN has attracted a lot of attention both in academia and industry. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of RIS-empowered SATN with NOMA. In particular, the rudimentary knowledge of SATN, NOMA scheme, and RIS technology is presented. Then, the motivations for investigating the NOMA-RIS-assisted SATN are discussed. In addition, we introduce the three usage modes of RIS, two scenarios of NOMA-RIS, and the path loss model of NOMA-RIS-assisted SATN. Next, the system performance is analyzed for a case study. Besides, a comprehensive overview of resource allocation in NOMA-RIS-assisted SATN is provided, where theoretical and artificial intelligence-based methods are compared and analyzed. Moreover, physical layer security and covert communication are selected as two representative security techniques to be discussed in NOMA-RIS-aided SATN. Furthermore, the combination of other emerging technologies with NOMA-RIS-assisted SATN is investigated. Finally, this survey provides a detailed discussion of the main challenges and open issues that need to be deeply investigated from a practical point of view, including channel modeling, channel estimation, deployment strategies, and backhaul control.
@article{RISPDNOMA, title = {RIS-Empowered Satellite-Aerial-Terrestrial Networks With PD-NOMA}, author = {Liu, Rui and Guo, Kefeng and Li, Xingwang and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Tsiftsis, Theodoros A. and Song, Houbing}, journal = {IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/COMST.2024.3393612}, volume = {26}, pages = {2258-2289}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Hybrid Conv-Attention Networks for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery-Based Target RecognitionJiseok Yoon, Jeongheon Song, Tanveer Hussain, and 3 more authorsIEEE Access, 2024
Hybrid Conv-Attention Networks for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery-Based Target RecognitionJiseok Yoon, Jeongheon Song, Tanveer Hussain, and 3 more authorsIEEE Access, 2024In this study, we propose hybrid conv-attention networks that combine convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformers to recognize targets from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images automatically. The proposed model is designed to obtain robust features from global and local patterns in the SAR image, utilizing the weights of a pre-trained backbone model with self-attention structures. Furthermore, we adopted pre-processing and training methods optimized for transfer learning to enhance performance. By comparing and analyzing the performance between the proposed model and conventional models using the OpenSARShip and MSTAR dataset, we found that our system significantly outperforms conventional approaches, with a performance improvement of 24.06%. This considerable enhancement is attributed to the ability of the model to leverage the 2D kernel-based approach of CNNs and the sequence vector-based approach of transformers, offering a comprehensive method for SAR image target recognition.
@article{HCATTN, title = {Hybrid Conv-Attention Networks for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery-Based Target Recognition}, author = {Yoon, Jiseok and Song, Jeongheon and Hussain, Tanveer and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Muhammad, Khan and Lee, Ik Hyun}, journal = {IEEE Access}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3387314}, volume = {12}, pages = {53045-53055}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 ZETA: ZEro-Trust Attack Framework with Split Learning for Autonomous Vehicles in 6G NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2024
ZETA: ZEro-Trust Attack Framework with Split Learning for Autonomous Vehicles in 6G NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2024In past, due to data and model security concerns, modern communication systems mainly focus on the use of edge computing devices for enabling immersive applications and services. Federated learning is one of the preferred solutions but it stresses the computation capability of the edge devices for immersive applications. Much research is now focusing on split learning as an alternative due to its ability of performing joint training with limited computing resources. However, split learning is also vulnerable to data reconstruction, feature space hijacking, and model inversion attacks, which are quite common concerning immersive applications such as Metaverse. In this regard, we propose a ZEro-Trust Attack (ZETA) framework for data reconstruction and model inversion attacks for autonomous vehicles opting for split learning strategies. We propose the joint training of client, server, and shadow models for both the reconstruction and main task to fool existing methods. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method is capable of reconstructing client’s data with an error of 0.0032. This study is proposed as a basis to design more sophisticated defense mechanisms for autonomous vehicles to protect user services in 5G/6G networks.
@inproceedings{ZETA2024, title = {ZETA: ZEro-Trust Attack Framework with Split Learning for Autonomous Vehicles in 6G Networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Singh, Keshav and Nkenyereye, Lewis and Kilper, Dan}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC)}, pages = {1-6}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/WCNC57260.2024.10571158}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 SLIP: Self-Supervised Learning Based Model Inversion and Poisoning Detection-Based Zero-Trust Systems for Vehicular NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Parus Khowaja, and 2 more authorsIEEE Wireless Communications, 2024
SLIP: Self-Supervised Learning Based Model Inversion and Poisoning Detection-Based Zero-Trust Systems for Vehicular NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Parus Khowaja, and 2 more authorsIEEE Wireless Communications, 2024The advances in communication networks and their integration with machine learning technology have paved the way for ubiquitous and prediction-based services for consumers. However, these services consider sensitive and private data for training a machine learning model. With the emergence of model inversion and poisoning attacks, sensitive and private data can be leaked, which is a hindrance for the realization of largescale automation services concerning communication networks. Zero-trust techniques allow the networks to rate the data for their participation in service provisioning tasks, but existing works do not consider model privacy for the zero-trust services. This article proposes a Self-supervised Learning based model Inversion and Poisoning (SLIP) detection framework that enables the rating of model so that network could decide whether the model is suitable for service provisioning or has been compromised. The framework leverages several Generative AI technologies such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models, to realize its implementation in federated learning setting. Experimental results show that the SLIP framework helps in reducing model inversion and poisoning attacks by 16.4% and 13.2% for vehicular networks, respectively.
@article{SLIP2024, title = {SLIP: Self-Supervised Learning Based Model Inversion and Poisoning Detection-Based Zero-Trust Systems for Vehicular Networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Nkenyereye, Lewis and Khowaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Niyato, Dusit}, journal = {IEEE Wireless Communications}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MWC.001.2300377}, volume = {31}, pages = {50-57}, dimensions = {true}, } -
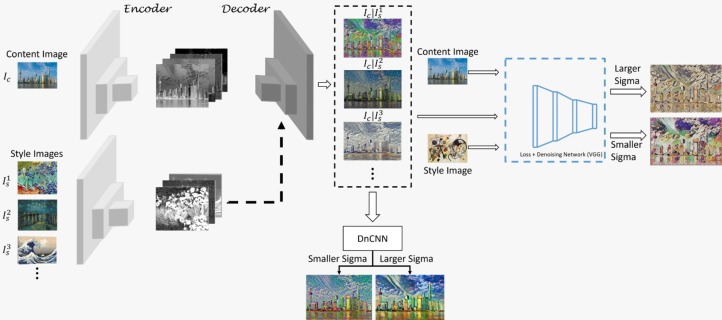 Extending user control for image stylization using hierarchical style transfer networksSunder Ali Khowaja, Sultan Almakdi, Muhammad Ali Memon, and 5 more authorsHeliyon, 2024
Extending user control for image stylization using hierarchical style transfer networksSunder Ali Khowaja, Sultan Almakdi, Muhammad Ali Memon, and 5 more authorsHeliyon, 2024The field of neural style transfer refers to the re-rendering of content image while fusing the features of a style image. The recent studies either focus on multiple style transfer or arbitrary style transfer while using perceptual and fixpoint content losses in their respective network architectures. The aforementioned losses provide notable stylization results but lack the liberty of style control to the user. Consequently, the stylization results also compromise the preservation of details with respect to the content image. This work proposes the hierarchical style transfer network (HSTN) for the image stylization task that could provide the user with the liberty to control the degree of incurred style via denoising parameter. The HSTN incorporates the proposed fixpoint control loss that preserves details from the content image and the addition of denoising CNN network (DnCNN) and denoising loss for allowing the user to control the level of stylization. The encoder-decoder block, the DnCNN block, and the loss network block make the basic building blocks of HSTN. Extensive experiments have been carried out, and the results are compared with existing works to demonstrate the effectiveness of HSTN. The subjective user evaluation shows that the HSTN’s stylization represents the best fusion of style and generates unique stylization results while preserving the content image details, which is evident by acquiring 12% better results than the second-best performing method. It has also been observed that the proposed work is amongst the studies that achieve the best trade-off regarding content and style classification scores, i.e. 37.64% and 60.27%, respectively.
@article{ImageStyle, title = {Extending user control for image stylization using hierarchical style transfer networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Almakdi, Sultan and Memon, Muhammad Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Sulaiman, Adel and Alqahtani, Ali and Shaikh, Asadullah and Alghamdi, Abdullah}, journal = {Heliyon}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Cell Press}, doi = {10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27012}, volume = {10}, pages = {e27012}, dimensions = {true}, } -
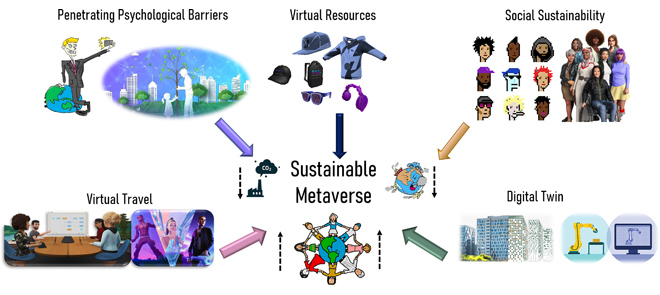 AI and 6G Into the Metaverse: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research TrendsMuhammad Zawish, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2024
AI and 6G Into the Metaverse: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research TrendsMuhammad Zawish, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2024Since Facebook was renamed Meta, a lot of attention, debate, and exploration have intensified about what the Metaverse is, how it works, and the possible ways to exploit it. It is anticipated that Metaverse will be a continuum of rapidly emerging technologies, usecases, capabilities, and experiences that will make it up for the next evolution of the Internet. Several researchers have already surveyed the literature on artificial intelligence (AI) and wireless communications in realizing the Metaverse. However, due to the rapid emergence and continuous evolution of technologies, there is a need for a comprehensive and in-depth survey of the role of AI, 6G, and the nexus of both in realizing the immersive experiences of Metaverse. Therefore, in this survey, we first introduce the background and ongoing progress in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MR) and spatial computing, followed by the technical aspects of AI and 6G. Then, we survey the role of AI in the Metaverse by reviewing the state-of-the-art in deep learning, computer vision, and Edge AI to extract the requirements of 6G in Metaverse. Next, we investigate the promising services of B5G/6G towards Metaverse, followed by identifying the role of AI in 6G networks and 6G networks for AI in support of Metaverse applications, and the need for sustainability in Metaverse. Finally, we enlist the existing and potential applications, usecases, and projects to highlight the importance of progress in the Metaverse. Moreover, in order to provide potential research directions to researchers, we underline the challenges, research gaps, and lessons learned identified from the literature review of the aforementioned technologies.
@article{AI6GMetaverse, title = {AI and 6G Into the Metaverse: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research Trends}, author = {Zawish, Muhammad and Dharejo, Fayaz Ali and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Raza, Saleem and Davy, Steven and Dev, Kapal and Bellavista, Paolo}, journal = {IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27012}, volume = {5}, pages = {730-778}, dimensions = {true}, }
2023
-
 FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-Based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained DevicesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023
FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-Based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained DevicesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023Generating video highlights in the form of animated graphics interchange formats (GIFs) has significantly simplified the process of video browsing. Animated GIFs have paved the way for applications concerning streaming platforms and emerging technologies. Existing studies have led to large computational complexity without considering user personalization. This paper proposes lightweight method to attract users and increase views of videos through personalized artistic media, i.e., static thumbnails and animated GIF generation. The proposed method analyzes lightweight thumbnail containers (LTC) using the computational resources of the client device to recognize personalized events from feature-length sports videos. Next, the thumbnails are then ranked through the frame rank pooling method for their selection. Subsequently, the proposed method processes small video segments rather than considering the whole video for generating artistic media. This makes our approach more computationally efficient compared to existing methods that use the entire video data; thus, the proposed method complies with sustainable development goals. Furthermore, the proposed method retrieves and uses thumbnail containers and video segments, which reduces the required transmission bandwidth as well as the amount of locally stored data. Experiments reveal that the computational complexity of our method is 3.73 times lower than that of the state-of-the-art method.
@article{FRCGIF, title = {FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-Based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained Devices}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Jarwar, Muhammad Aslam and Choi, Jaehyuk and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Big Data}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TBDATA.2023.3338012}, volume = {10}, pages = {343-355}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 DASTAN-CNN: RF Fingerprinting for the Mitigation of Membership Inference Attacks in 5GSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIn GLOBECOM 2023 - 2023 IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2023
DASTAN-CNN: RF Fingerprinting for the Mitigation of Membership Inference Attacks in 5GSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIn GLOBECOM 2023 - 2023 IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2023The fifth generation (5G) networks are designed to support a large range of diverse services with strict performance requirements. Studies suggest that, 5G uses machine learning technologies for variety of tasks ranging from network management, and resource optimization to automated services. The successful integration of 5G with machine learning has also led to the basis for 6G networks. However, the use of machine learning makes the 5G networks susceptible to adversarial attacks. A few works study the effect of differential privacy and adversarial attacks in the 5G systems let alone to provide the proposal of effective defense mechanism. This study proposes Denoising and Adversarial attack-based STacked AutoeNcoder (DASTAN) convolutional neural networks (CNN) to provide defense against a specific differential privacy attack, i.e. membership inference, optimized to detect the device or data distribution potentially used in the training process. DASTAN initiates an intentional attack to camouflage the characteristics of an authorized user from an adversary and uses a de noising stacked autoencoder to recover the information at service provider’s end for RF fingerprinting. The aim of RF fingerprinting is to validate the authenticity and identity of the device to preserve the privacy of wireless network. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of DASTAN-CNN, which reduces the attack success rate by up to 52.69% in comparison to the case where no defense strategy is employed. The DASTAN-CNN also achieves 75.29% authorized user recognition rate for RF fingerprinting while reducing the attack success rate to 39.23%, which shows the effectiveness in terms of trade-off efficiency.
@inproceedings{DASTAN, title = {DASTAN-CNN: RF Fingerprinting for the Mitigation of Membership Inference Attacks in 5G}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Antonopoulos, Angelos and Magarini, Maurizio}, booktitle = {GLOBECOM 2023 - 2023 IEEE Global Communications Conference}, pages = {5524-5529}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/GLOBECOM54140.2023.10437263}, dimensions = {true}, } -
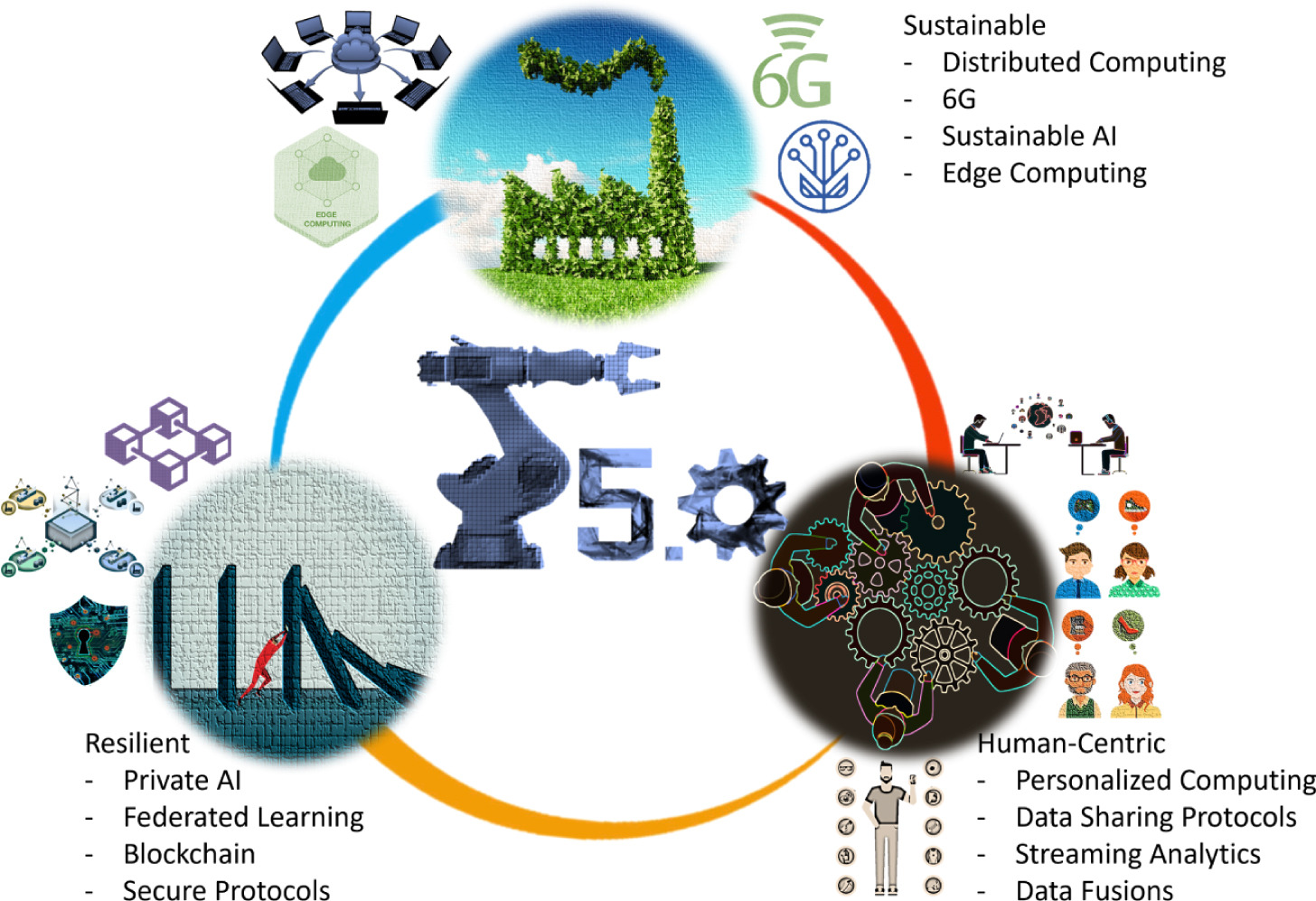 Towards defining industry 5.0 vision with intelligent and softwarized wireless network architectures and services: A surveyShah Zeb, Aamir Mahmood, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023
Towards defining industry 5.0 vision with intelligent and softwarized wireless network architectures and services: A surveyShah Zeb, Aamir Mahmood, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023Industry 5.0 vision, a step toward the next industrial revolution and enhancement to Industry 4.0, conceives the new goals of resilient, sustainable, and human-centric approaches in diverse emerging applications such as factories-of-the-future and digital society. The vision seeks to leverage human intelligence and creativity in nexus with intelligent, efficient, and reliable cognitive collaborating robots (cobots) to achieve zero waste, zero-defect, and mass customization-based manufacturing solutions. However, it requires merging distinctive cyber–physical worlds through intelligent orchestration of various technological enablers, e.g., cognitive cobots, human-centric artificial intelligence (AI), cyber–physical systems, digital twins, hyperconverged data storage and computing, communication infrastructure, and others. In this regard, the convergence of the emerging computational intelligence (CI) paradigm and softwarized next-generation wireless networks (NGWNs) can fulfill the stringent communication and computation requirements of the technological enablers of the Industry 5.0, which is the aim of this survey. In this article, we address this issue by reviewing and analyzing current emerging concepts and technologies, e.g., CI tools and frameworks, network-in-box architecture, open radio access networks, softwarized service architectures, potential enabling services, and others, elemental and holistic for designing the objectives of CI-NGWNs to fulfill the Industry 5.0 vision requirements. Furthermore, we outline and discuss ongoing initiatives, demos, and frameworks linked to Industry 5.0. Finally, we provide a list of lessons learned from our detailed review, research challenges, and open issues that should be addressed in CI-NGWNs to realize Industry 5.0.
@article{Industry5, title = {Towards defining industry 5.0 vision with intelligent and softwarized wireless network architectures and services: A survey}, author = {Zeb, Shah and Mahmood, Aamir and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Hassan, Syed Ali and Gidlund, Mikael and Bellavista, Paolo}, journal = {Journal of Network and Computer Applications}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.jnca.2023.103796}, volume = {223}, pages = {103796}, dimensions = {true}, } -
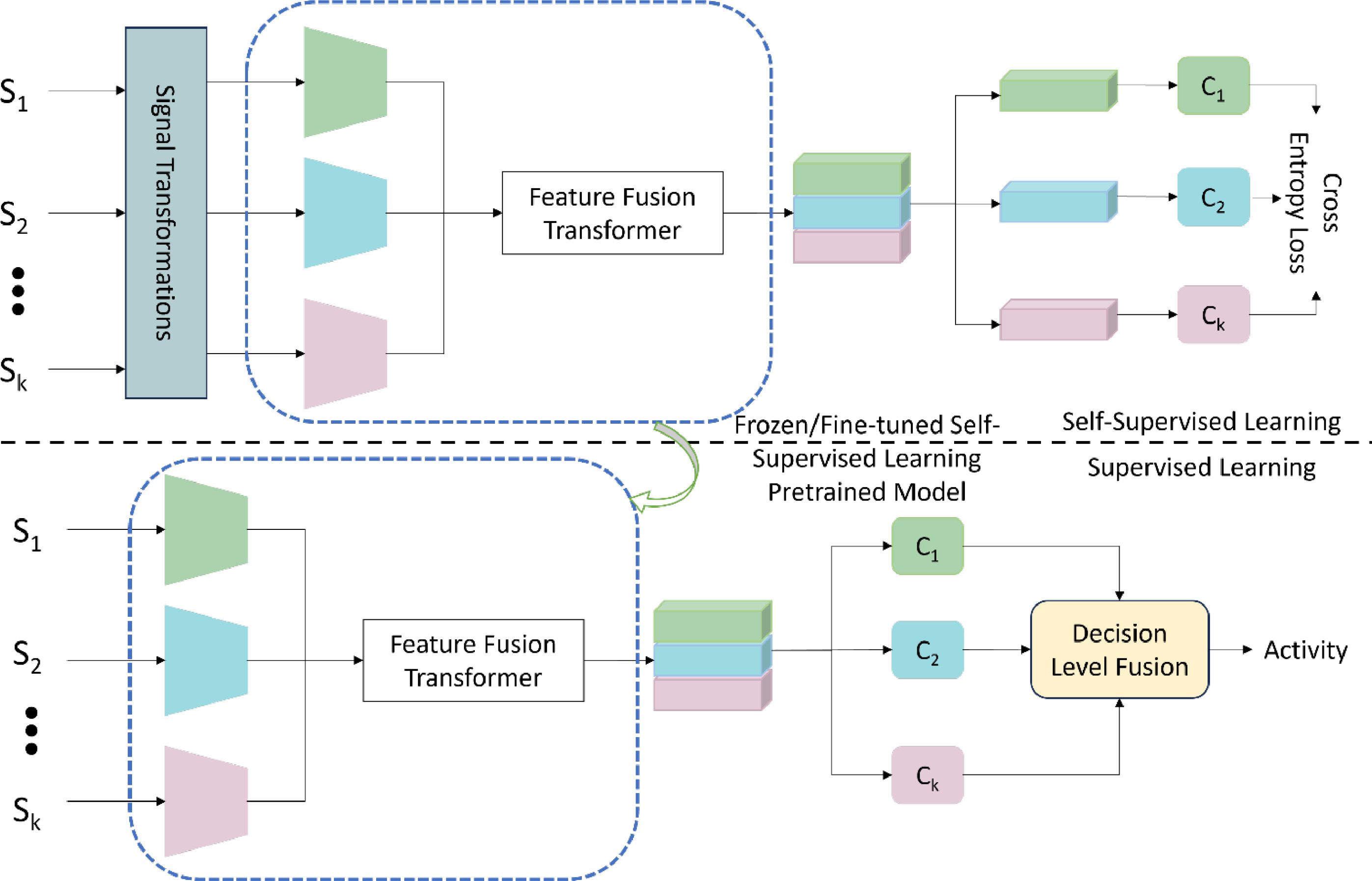 ReFuSeAct: Representation fusion using self-supervised learning for activity recognition in next generation networksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, and 4 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2023
ReFuSeAct: Representation fusion using self-supervised learning for activity recognition in next generation networksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, and 4 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2023Over the years, wearable sensors have gained a lot of attention from the research community due to their non-invasive nature, adoption of sensors by general public, and their applicability in healthcare services. With the advancements in communication networks, machine learning methods, and wearable sensor deployment, it is essential to design a method that could accurately classify human activities while reducing the dependence on annotated data. Traditional machine learning approaches require large-scale annotated data in order to provide a reasonable recognition performance. Recently, self-supervised learning methods are proposed but they are either limited to single sensor devices or fail to model intra-modal correlations within the self-supervised learning paradigm. In this work, we propose Representation Fusion using Self-supervised learning for Activity Recognition (ReFuSeAct) framework that uses modality-specific encoders, attention encoders, and decision-level fusion strategies to address the aforementioned limitations. The self-supervised learning paradigm ensures that the method achieves better performance even with less amount of annotated data. The architecture proposed for modality-specific encoder ensures that extraction of representative features that could help in improving recognition performance. The feature-level fusion performed using the proposed attention encoders enhances the quality of representative features that could be used in supervised learning phase. Finally, the decision-level fusion strategy enhances the activity recognition accuracy in comparison to the single deep learning classifier. Our experimental analysis shows that the proposed approach records 9.1% improvement over semi-supervised learning baselines and more than 2% improvement in comparison to existing self-supervised learning approaches.
@article{RefuseAct, title = {ReFuSeAct: Representation fusion using self-supervised learning for activity recognition in next generation networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dharejo, Fayaz Ali and Raza, Saleem and Lee, Ik Hyun and Naqvi, Rizwan Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {Information Fusion}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102044}, volume = {102}, pages = {102044}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Spike learning based Privacy Preservation of Internet of Medical Things in MetaverseSunder Ali Khowaja, Kamran Dahri, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 1 more authorIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Healthcare Informatics, 2023
Spike learning based Privacy Preservation of Internet of Medical Things in MetaverseSunder Ali Khowaja, Kamran Dahri, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 1 more authorIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Healthcare Informatics, 2023With the rising trend of digital technologies, such as augmented and virtual reality, Metaverse has gained a notable popularity. The applications that will eventually benefit from Metaverse is the telemedicine and e-health fields. However, the data and techniques used for realizing the medical side of Metaverse is vulnerable to data and class leakage attacks. Most of the existing studies focus on either of the problems through encryption techniques or addition of noise. In addition, the use of encryption techniques affects the overall performance of the medical services, which hinders its realization. In this regard, we propose Generative adversarial networks and spike learning based convolutional neural network (GASCNN) for medical images that is resilient to both the data and class leakage attacks. We first propose the GANs for generating synthetic medical images from residual networks feature maps. We then perform a transformation paradigm to convert ResNet to spike neural networks (SNN) and use spike learning technique to encrypt model weights by representing the spatial domain data into temporal axis, thus making it difficult to be reconstructed. We conduct extensive experiments on publicly available MRI dataset and show that the proposed work is resilient to various data and class leakage attacks in comparison to existing state-of-the-art works (1.75x increase in FID score) with the exception of slightly decreased performance (less than 3%) from its ResNet counterpart. while achieving 52x energy efficiency gain with respect to standard ResNet architecture.
@article{Spike, title = {Spike learning based Privacy Preservation of Internet of Medical Things in Metaverse}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dahri, Kamran and Jarwar, Muhammad Aslam and Lee, Ik Hyun}, journal = {IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Healthcare Informatics}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JBHI.2023.3306704}, volume = {Early Access}, pages = {1-8}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution (×4): Methods and ResultsYulun Zhang, Kai Zhang, Zheng Chen, and 75 more authorsIn 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2023
NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution (×4): Methods and ResultsYulun Zhang, Kai Zhang, Zheng Chen, and 75 more authorsIn 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2023This paper reviews the NTIRE 2023 challenge on image super-resolution (×4), focusing on the proposed solutions and results. The task of image super-resolution (SR) is to generate a high-resolution (HR) output from a corresponding low-resolution (LR) input by leveraging prior information from paired LR-HR images. The aim of the challenge is to obtain a network design/solution capable to produce high-quality results with the best performance (e.g., PSNR). We want to explore how high performance we can achieve regardless of computational cost (e.g., model size and FLOPs) and data. The track of the challenge was to measure the restored HR images with the ground truth HR images on DIV2K testing dataset. The ranking of the teams is determined directly by the PSNR value. The challenge has attracted 192 registered participants, where 15 teams made valid submissions. They achieve state-of-the-art performance in single image super-resolution.
@inproceedings{NTIREx4, title = {NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution (×4): Methods and Results}, author = {Zhang, Yulun and Zhang, Kai and Chen, Zheng and Li, Yawei and Timofte, Radu and Zhang, Junpei and Zhang, Kexin and Peng, Rui and Ma, Yanbiao and Jia, Licheng and Huang, Huaibo and Zhou, Xiaoqiang and Ai, Yuang and He, Ran and Qiu, Yajun and Zhu, Qiang and Li, Pengfei and Li, Qianhui and Zhu, Shuyuan and Zhang, Dafeng and Li, Jia and Wang, Fan and Li, Chunmiao and Kim, TaeHyung and Kil, Jungkeong and Kim, Eon and Yu, Yeonseung and Lee, Beomyeol and Lee, Subin and Lim, Seokjae and Chae, Somi and Choi, Heungjun and Huang, ZhiKai and Chen, YiChung and Chiang, YuanChun and Yang, HaoHsiang and Chen, WeiTing and Chang, HuaEn and Chen, I-Hsiang and Hsieh, ChiaHsuan and Kuo, SyYen and Choi, Ui-Jin and Conde, Marcos V. and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Yoon, Jiseok and Lee, Ik Hyun and Gendy, Garas and Sabor, Nabil and Hou, Jingchao and He, Guanghui and Zhang, Zhao and Li, Baiang and Zheng, Huan and Zhao, Suiyi and Gao, Yangcheng and Wei, Yanyan and Ren, Jiahuan and Wei, Jiayu and Li, Yanfeng and Sun, Jia and Cheng, Zhanyi and Li, Zhiyuan and Yao, Xu and Wang, Xinyi and Li, Danxu and Cui, Xuan and Cao, Jun and Li, Cheng and Zheng, Jianbin and Sarvaiya, Anjali and Prajapati, Kalpesh and Patra, Ratnadeep and Barik, Pragnesh and Rathod, Chaitanya and Upla, Kishor and Raja, Kiran and Ramachandra, Raghavendra and Busch, Christoph}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)}, pages = {1865-1884}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00185}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Denoising: Methods and ResultsYawei Li, Yulun Zhang, Radu Timofte, and 78 more authorsIn 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2023
NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Denoising: Methods and ResultsYawei Li, Yulun Zhang, Radu Timofte, and 78 more authorsIn 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2023This paper reviews the NTIRE 2023 challenge on image denoising (σ = 50) with a focus on the proposed solutions and results. The aim is to obtain a network design capable to produce high-quality results with the best performance measured by PSNR for image denoising. Independent additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is assumed and the noise level is 50. The challenge had 225 registered participants, and 16 teams made valid submissions. They gauge the state-of-the-art for image denoising.
@inproceedings{NTIREdenoise, title = {NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Image Denoising: Methods and Results}, author = {Li, Yawei and Zhang, Yulun and Timofte, Radu and Gool, Luc Van and Tu, Zhijun and Du, Kunpeng and Wang, Hailing and Chen, Hanting and Li, Wei and Wang, Xiaofei and Hu, Jie and Wang, Yunhe and Kong, Xiangyu and Wu, Jinlong and Zhang, Dafeng and Zhang, Jianxing and Liu, Shuai and Bai, Furui and Feng, Chaoyu and Wang, Hao and Zhang, Yuqian and Shao, Guangqi and Wang, Xiaotao and Lei, Lei and Xu, Rongjian and Zhang, Zhilu and Chen, Yunjin and Ren, Dongwei and Zuo, Wangmeng and Wu, Qi and Han, Mingyan and Cheng, Shen and Li, Haipeng and Jiang, Ting and Jiang, Chengzhi and Li, Xinpeng and Luo, Jinting and Lin, Wenjie and Yu, Lei and Fan, Haoqiang and Liu, Shuaicheng and Arora, Aditya and Zamir, Syed Waqas and Vazquez-Corral, Javier and Derpanis, Konstantinos G. and Brown, Michael S. and Li, Hao and Zhao, Zhihao and Pan, Jinshan and Dong, Jiangxin and Tang, Jinhui and Yang, Bo and Chen, Jingxiang and Li, Chenghua and Zhang, Xi and Zhang, Zhao and Ren, Jiahuan and Ji, Zhicheng and Miao, Kang and Zhao, Suiyi and Zheng, Huan and Wei, YanYan and Liu, Kangliang and Du, Xiangcheng and Liu, Sijie and Zheng, Yingbin and Wu, Xingjiao and Jin, Cheng and Irny, Rajeev and Koundinya, Sriharsha and Kamath, Vighnesh and Khandelwal, Gaurav and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Yoon, Jiseok and Lee, Ik Hyun and Chen, Shijie and Zhao, Chengqiang and Yang, Huabin and Zhang, Zhongjian and Huang, Junjia and Zhang, Yanru}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)}, pages = {1905-1921}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00188}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Multikeyword-Ranked Search Scheme Supporting Extreme Environments for Internet of VehiclesDequan Xu, Changgen Peng, Weizheng Wang, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023
Multikeyword-Ranked Search Scheme Supporting Extreme Environments for Internet of VehiclesDequan Xu, Changgen Peng, Weizheng Wang, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023In recent years, the cloud infrastructure has been developed as a promising sharing system for the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) communication. During the information exchange, search service over ciphertext called searchable encryption (SE) is an extraordinary method to prevent data breaches. However, two open problems still need to be solved for ranked search, which hinders the application practicality in IoV. First, each data owner must store the extra information to distribute weight values dynamically. Second, ranking in the cloud has not been supported by most existing schemes. In this article, to address the above problems and fit the characteristics of real-time data exchange in IoV, we present a multikeyword-ranked search scheme supporting extreme environments for the IoV. Specifically, our system designs a unique encrypted index tree structure to realize the multikeyword-ranked retrieval, the weight value dynamic adaptive calculation, and dynamic updating in IoV. Moreover, we use a primary–secondary dual-server model to cope with extreme environments and propose a “greedy breadth-first search” algorithm to achieve an effective sublinear search. Finally, comprehensive security analysis and experimental simulation for the proposed system prove that our system can guarantee user privacy and acceptable efficiency.
@article{Multikeyword, title = {Multikeyword-Ranked Search Scheme Supporting Extreme Environments for Internet of Vehicles}, author = {Xu, Dequan and Peng, Changgen and Wang, Weizheng and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Tian, Youliang}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2023.3275386}, volume = {11}, pages = {3868-3880}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 SPIN: Simulated Poisoning and Inversion Network for Federated Learning-Based 6G Vehicular NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIn ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2023
SPIN: Simulated Poisoning and Inversion Network for Federated Learning-Based 6G Vehicular NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIn ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2023The applications concerning vehicular networks benefit from the vision of beyond 5G and 6G technologies such as ultra-dense network topologies, low latency, and high data rates. Vehicular networks have always faced data privacy preservation concerns, which lead to the advent of distributed learning techniques such as federated learning. Although federated learning has solved data privacy preservation issues to some extent, the technique is quite vulnerable to model inversion and model poisoning attacks. We assume that the design of defense mechanism and attacks are two sides of the same coin. Designing a method to reduce vulnerability requires the attack to be effective and challenging with real-world implications. In this work, we propose simulated poisoning and inversion network (SPIN) that leverages the optimization approach for reconstructing data from a differential model trained by a vehicular node and intercepted when transmitted to roadside unit (RSU). We then train a generative adversarial network (GAN) to improve the generation of data with each passing round and global update from the RSU, accordingly. Evaluation results show the qualitative and quantitative effectiveness of the proposed approach. The attack initiated by SPIN can reduce up to 22% accuracy on publicly available datasets while just using a single attacker. We assume that revealing the simulation of such attacks would help us find its defense mechanism in an effective manner.
@inproceedings{SPIN, title = {SPIN: Simulated Poisoning and Inversion Network for Federated Learning-Based 6G Vehicular Networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Antonopoulos, Angelos}, booktitle = {ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications}, pages = {6205-6210}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10279339}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Smart Navigation and Energy Management Framework for Autonomous Electric Vehicles in Complex EnvironmentsGunasekaran Raja, Gayathri Saravanan, Sahaya Beni Prathiba, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023
Smart Navigation and Energy Management Framework for Autonomous Electric Vehicles in Complex EnvironmentsGunasekaran Raja, Gayathri Saravanan, Sahaya Beni Prathiba, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023Autonomous electric vehicles (AEVs) are revolutionizing the world of smart city transportation due to their low-resource consumption, improved traffic efficiency, zero carbon emissions, and improved road safety. To ensure the safe passage of vehicles through a complex environment, it is essential to plan for safe and smart navigation and energy management for AEVs. This demands an effective model for locating the optimal electric charging stations (ECSs) for scheduling and recharging the AEVs when they run on low battery. Many research works, however, do not focus on navigation and scheduling policies for AEV charging that would occur in extreme events in complex environments. This article puts forth a collaborative optimal navigation and charge planning (CONCP) framework based on multiagent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL). To ensure the safe passage of vehicles through the complex environment, it is essential to plan for safe and smart navigation and energy management for AEVs. The CONCP framework aims to achieve the best route from the origin to the final destination for each AEV, scheduling the optimal ECS while avoiding obstacles, reducing traffic congestion, and maximizing energy efficiency, accordingly. The experimental results indicate that CONCP achieves 27% higher success rates, 31% fewer collision rates, and 37% higher reward per episode than the other state-of-the-art algorithms.
@article{SmartNavigation, title = {Smart Navigation and Energy Management Framework for Autonomous Electric Vehicles in Complex Environments}, author = {Raja, Gunasekaran and Saravanan, Gayathri and Prathiba, Sahaya Beni and Akhtar, Zahid and Ali Khowaja, Sunder and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2023.3244854}, volume = {10}, pages = {18641-18650}, dimensions = {true}, }
2022
-
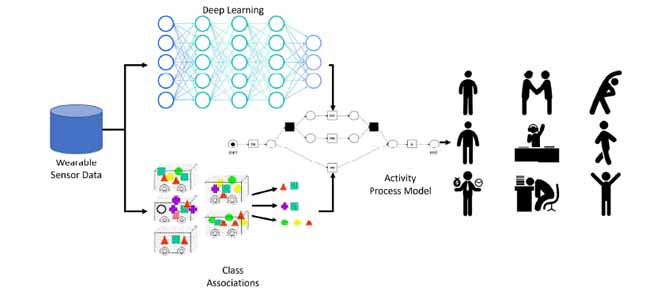 PROMPT: Process Mining and Paravector Tensor-Based Physical Health Monitoring FrameworkSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Sensors Journal, 2022
PROMPT: Process Mining and Paravector Tensor-Based Physical Health Monitoring FrameworkSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorIEEE Sensors Journal, 2022The provision of physical healthcare services during the isolation phase is one of the major challenges associated with the current COVID-19 pandemic. Smart healthcare services face a major challenge in the form of human behavior, which is based on human activities, complex patterns, and subjective nature. Although the advancement in portable sensors and artificial intelligence has led to unobtrusive activity recognition systems, very few studies deal with behavior tracking for addressing the problem of variability and behavior dynamics. In this regard, we propose the fusion of PRocess mining and Paravector Tensor (PROMPT)-based physical health monitoring framework that not only tracks subjective human behavior, but also deals with the intensity variations associated with inertial measurement units. Our experimental analysis of a publicly available dataset shows that the proposed method achieves 14.56% better accuracy in comparison to existing works. We also propose a generalized framework for healthcare applications using wearable sensors and the PROMPT method for its triage with physical health monitoring systems in the real world.
@article{PROMPT, title = {PROMPT: Process Mining and Paravector Tensor-Based Physical Health Monitoring Framework}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Jarwar, Muhammad Aslam}, journal = {IEEE Sensors Journal}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JSEN.2022.3195613}, volume = {23}, pages = {989-996}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Spatiotemporal Prediction Based Intelligent Task Allocation for Secure Spatial Crowdsourcing in Industrial IoTMengyao Peng, Jia Hu, Hui Lin, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022
Spatiotemporal Prediction Based Intelligent Task Allocation for Secure Spatial Crowdsourcing in Industrial IoTMengyao Peng, Jia Hu, Hui Lin, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022With the emergence of spatial crowdsourcing technology, an efficient task allocation is the key to ensure the sustainable development of spatial crowdsourcing. However, previous spatial crowdsourcing task allocation technologies ignore the temporal and spatial continuity between historical task data, thus reducing the efficiency of crowdsourcing task allocation. In addition, spatial crowdsourcing also suffers from the privacy leakage problem. To solve these problems, we propose a Spatiotemporal Prediction based Spatial Crowdsourcing strategy, named SPSC, using both blockchain and artificial intelligence. Specifically, considering the temporal and spatial continuity of crowdsourced task data, SPSC combines both gated recurrent unit and variational autoencoder for crowdsourcing task prediction. In addition, different Laplacian noises are added to crowdsourced task data so as to protect the privacy of crowdsourced workers during the task prediction. Moreover, by classifying crowdsourcing tasks and grouping crowdsourcing workers, SPSC reduces the risk of crowdsourcing workers colluding to steal the privacy data of crowdsourcing tasks using the blockchain technology. The experimental results show that SPSC can improve the privacy protection of spatial crowdsourcing, specifically, the more the number of categories, the higher the degree of privacy protection, and under the premise of predicting value, excellent system performance can be achieved.
@article{TNSE20232, title = {Spatiotemporal Prediction Based Intelligent Task Allocation for Secure Spatial Crowdsourcing in Industrial IoT}, author = {Peng, Mengyao and Hu, Jia and Lin, Hui and Wang, Xiaoding and Liu, Peng and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TNSE.2022.3198675}, volume = {10}, pages = {2853-2863}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 A Secure Data Sharing Scheme in Community Segmented Vehicular Social Networks for 6GSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022
A Secure Data Sharing Scheme in Community Segmented Vehicular Social Networks for 6GSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022The use of aerial base stations, AI cloud, and satellite storage can help manage location, traffic, and specific application-based services for vehicular social networks. However, sharing of such data makes the vehicular network vulnerable to data and privacy leakage. In this regard, this article proposes an efficient and secure data sharing scheme using community segmentation and a blockchain-based framework for vehicular social networks. The proposed work considers similarity matrices that employ the dynamics of structural similarity, modularity matrix, and data compatibility. These similarity matrices are then passed through stacked autoencoders that are trained to extract encoded embedding. A density-based clustering approach is then employed to find the community segments from the information distances between the encoded embeddings. A blockchain network based on the Hyperledger Fabric platform is also adopted to ensure data sharing security. Extensive experiments have been carried out to evaluate the proposed data-sharing framework in terms of the sum of squared error, sharing degree, time cost, computational complexity, throughput, and CPU utilization for proving its efficacy and applicability. The results show that the CSB framework achieves a higher degree of SD, lower computational complexity, and higher throughput.
@article{CSVSocial, title = {A Secure Data Sharing Scheme in Community Segmented Vehicular Social Networks for 6G}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and Lee, Ik Hyun and Khan, Wali Ullah and Wang, Weizheng and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh and Magarini, Maurizio}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TII.2022.3188963}, volume = {19}, pages = {890-899}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Multimodal-Boost: Multimodal Medical Image Super-Resolution Using Multi-Attention Network With Wavelet TransformFayaz Ali Dharejo, Muhammad Zawish, Farah Deeba, and 4 more authorsIEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2022
Multimodal-Boost: Multimodal Medical Image Super-Resolution Using Multi-Attention Network With Wavelet TransformFayaz Ali Dharejo, Muhammad Zawish, Farah Deeba, and 4 more authorsIEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2022Multimodal medical images are widely used by clinicians and physicians to analyze and retrieve complementary information from high-resolution images in a non-invasive manner. Loss of corresponding image resolution adversely affects the overall performance of medical image interpretation. Deep learning-based single image super resolution (SISR) algorithms have revolutionized the overall diagnosis framework by continually improving the architectural components and training strategies associated with convolutional neural networks (CNN) on low-resolution images. However, existing work lacks in two ways: i) the SR output produced exhibits poor texture details, and often produce blurred edges, ii) most of the models have been developed for a single modality, hence, require modification to adapt to a new one. This work addresses (i) by proposing generative adversarial network (GAN) with deep multi-attention modules to learn high-frequency information from low-frequency data. Existing approaches based on the GAN have yielded good SR results; however, the texture details of their SR output have been experimentally confirmed to be deficient for medical images particularly. The integration of wavelet transform (WT) and GANs in our proposed SR model addresses the aforementioned limitation concerning textons. While the WT divides the LR image into multiple frequency bands, the transferred GAN uses multi-attention and upsample blocks to predict high-frequency components. Additionally, we present a learning method for training domain-specific classifiers as perceptual loss functions. Using a combination of multi-attention GAN loss and a perceptual loss function results in an efficient and reliable performance. Applying the same model for medical images from diverse modalities is challenging, our work addresses (ii) by training and performing on several modalities via transfer learning. Using two medical datasets, we validate our proposed SR network against existing state-of-the-art approaches and achieve promising results in terms of structural similarity index (SSIM) and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
@article{MultimodalBoost, title = {Multimodal-Boost: Multimodal Medical Image Super-Resolution Using Multi-Attention Network With Wavelet Transform}, author = {Dharejo, Fayaz Ali and Zawish, Muhammad and Deeba, Farah and Zhou, Yuanchun and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TCBB.2022.3191387}, volume = {20}, pages = {2420-2433}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Get Your Foes Fooled: Proximal Gradient Split Learning for Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks on IoMT DataSunder Ali Khowaja, Ik Hyun Lee, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022
Get Your Foes Fooled: Proximal Gradient Split Learning for Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks on IoMT DataSunder Ali Khowaja, Ik Hyun Lee, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022The past decade has seen a rapid adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI), specifically the deep learning networks, in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) ecosystem. However, it has been shown recently that the deep learning networks can be exploited by adversarial attacks that not only make IoMT vulnerable to the data theft but also to the manipulation of medical diagnosis. The existing studies consider adding noise to the raw IoMT data or model parameters which not only reduces the overall performance concerning medical inferences but also is ineffective to the likes of deep leakage from gradients method. In this work, we propose proximal gradient split learning (PSGL) method for defense against the model inversion attacks. The proposed method intentionally attacks the IoMT data when undergoing the deep neural network training process at client side. We propose the use of proximal gradient method to recover gradient maps and a decision-level fusion strategy to improve the recognition performance. Extensive analysis show that the PGSL not only provides effective defense mechanism against the model inversion attacks but also helps in improving the recognition performance on publicly available datasets. We report 14.0 % , 17.9 % , and 36.9 % gains in accuracy over reconstructed and adversarial attacked images, respectively.
@article{PGSL, title = {Get Your Foes Fooled: Proximal Gradient Split Learning for Defense Against Model Inversion Attacks on IoMT Data}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, Ik Hyun and Dev, Kapal and Jarwar, Muhammad Aslam and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TNSE.2022.3188575}, volume = {10}, pages = {2607-2616}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Skeleton-based human action recognition with sequential convolutional-LSTM networks and fusion strategiesSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022
Skeleton-based human action recognition with sequential convolutional-LSTM networks and fusion strategiesSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022Human action recognition from skeleton data has drawn a lot of attention from researchers due to the availability of thousands of real videos with many challenges. Existing works attempted to model the spatial characteristics and temporal dependencies of 3D joints using dynamic time warping, hand-crafted, and spatial co-occurrence features. However, the representation derived from the spatial stream overemphasizes the temporal information; thus, it yields limited expressive power. Some studies use skeleton sequences as frames to enhance the expressive power of representations but lose the generalization capability because the derived temporal smoothness is specific to a particular dataset. The proposed work uses joint distance maps as a base representation that encodes the spatial and temporal information to color texture images. We increase the expressive power by extracting the feature maps from pre-trained networks on ImageNet to diversify the texture representation and propose a network architecture to model the temporal dependency explicitly. We also explore various fusion strategies to generate diverse representations from the feature maps of the pre-trained networks. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves the best recognition accuracy when using decision-level fusion with meta-learners (Random Forest). The analysis also reveals that the use of feature-level fusion yields relatively good results in terms of the trade-off, i.e., on par recognition performance with some decision-level fusion strategies while having less tunable parameters. Extensive experimental results and comparative analysis on three benchmark datasets prove that the proposed representation and network not only yield better recognition accuracy but also exhibit stronger generalization capability on multiple datasets.
@article{Skeleton-LSTM, title = {Skeleton-based human action recognition with sequential convolutional-LSTM networks and fusion strategies}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = { Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing}, year = {2022}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s12652-022-03848-3}, volume = {13}, pages = {3729-3746}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 IIFNet: A Fusion-Based Intelligent Service for Noisy Preamble Detection in 6GSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Parus Khuwaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Network, 2022
IIFNet: A Fusion-Based Intelligent Service for Noisy Preamble Detection in 6GSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Parus Khuwaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Network, 2022In this article, we present our vision of preamble detection in a physical random access channel for next-generation (Next-G) networks using machine learning techniques. Preamble detection is performed to maintain communication and synchronization between devices of the Internet of Everything and next-generation nodes. Considering the scalability and traffic density, Next-G networks have to deal with preambles corrupted by noise due to channel characteristics or environmental constraints. We show that when injecting 15 percent random noise, the detection performance degrades to 48 percent. We propose an informative instance-based fusion Network (IIFNet) to cope with random noise and to improve detection performance simultaneously. A novel sampling strategy for selecting informa-tive instances from feature spaces has also been explored to improve detection performance. The proposed IIFNet is tested on a real dataset for preamble detection that was collected with the help of a reputable commercial company.
@article{IIFNet, title = {IIFNet: A Fusion-Based Intelligent Service for Noisy Preamble Detection in 6G}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Khuwaja, Parus and Pham, Quoc-Viet and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh and Bellavista, Paolo and Magarini, Maurizio}, journal = {IEEE Network}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MNET.004.2100527}, volume = {36}, pages = {48-54}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 In the Digital Age of 5G Networks: Seamless Privacy-Preserving Authentication for Cognitive-Inspired Internet of Medical ThingsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 3 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022
In the Digital Age of 5G Networks: Seamless Privacy-Preserving Authentication for Cognitive-Inspired Internet of Medical ThingsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 3 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022Cognitive-inspired Internet of Medical Things (CI-IoMT) combines cognitive science and artificial intelligence to interact with humans and ubiquitous digital environments. The Internet of Things devices generate massive amounts of data and process it with cognitive computing to perform efficient analysis at the edge nodes. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) uses the said analysis to design smart communication systems to facilitate ubiquitous services. However, the protocols used in IoMT use conventional number theory systems that are vulnerable to quantum-computer attacks. Therefore, an efficient CI-IoMT scheme is required to handle access privacy, preservation, and trust guarantee. This article presents an identity-based seamless privacy preservation (IB-SPP) for CI-IoMT to authorize smart device communications. It is entirely based on fast user authentication to shorten access timing in an emergency situation. The simulation analysis shows that the proposed IB-SPP scheme consumes less response time and minimum data volume than other existing schemes.
@article{DigitalAge, title = {In the Digital Age of 5G Networks: Seamless Privacy-Preserving Authentication for Cognitive-Inspired Internet of Medical Things}, author = {Deebak, B. D. and Memon, Fida Hussain and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Wang, Weizheng and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TII.2022.3172139}, volume = {18}, pages = {8916-8923}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Toward Industrial Private AI: A Two-Tier Framework for Data and Model SecuritySunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh Qureshi, and 2 more authorsIEEE Wireless Communications, 2022
Toward Industrial Private AI: A Two-Tier Framework for Data and Model SecuritySunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh Qureshi, and 2 more authorsIEEE Wireless Communications, 2022With the advances in 5G and IoT devices, industries are vastly adopting artificial intelligence (AI) techniques for improving classification and prediction-based services. However, the use of AI also raises concerns regarding data privacy and security that can be misused or leaked. Private AI was recently coined to address the data security issue by combining AI with encryption techniques, but existing studies have shown that model inversion attacks can be used to reverse engineer the images from model parameters. In this regard, we propose a federated learning and encryption-based private (FLEP) AI framework that provides two-tier security for data and model parameters in an Industrial IoT environment. We propose a three-layer encryption method for data security and provided a hypothetical method to secure the model parameters. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better encryption quality at the expense of slightly increased execution time. We also highlight several open issues and challenges regarding the FLEP AI framework’s realization.
@article{PrivateAI, title = {Toward Industrial Private AI: A Two-Tier Framework for Data and Model Security}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh and Khuwaja, Parus and Foschini, Luca}, journal = {IEEE Wireless Communications}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MWC.001.2100479}, volume = {29}, pages = {76-83}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 TAB-SAPP: A Trust-Aware Blockchain-Based Seamless Authentication for Massive IoT-Enabled Industrial ApplicationsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022
TAB-SAPP: A Trust-Aware Blockchain-Based Seamless Authentication for Massive IoT-Enabled Industrial ApplicationsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022The advancement of sensory technologies proliferates the development of low-cost electronics systems to operate the environmental features of smart cities. Global urbanization integrates networking systems to offer computing-based practical solutions for improving the quality of application-oriented services. Few existing studies have primarily focused on a single-point vulnerability for decentralized IoT applications. However, very few mechanisms address the issues concerning privacy-preserving and trust-aware authentication for IoT-enabled industrial applications. Moreover, the existing schemes are in fact not applicable to real-time scenarios, such as decentralized networks and long-term evolution advanced networks. Thus, this article presents a trust-aware blockchain-based seamless authentication with privacy-preserving (TAB-SAPP) to resolve the critical things, such as privacy, security, and packet delivery ratio. In the proposed TAB-SAPP, a novel data traffic pattern is utilized using identity management to show that the proposed mechanism can be more functional in expanding users’ connectivity to improve the communication metrics, such as packet delivery ratio and mobility speed.
@article{TAB-SAPP, title = {TAB-SAPP: A Trust-Aware Blockchain-Based Seamless Authentication for Massive IoT-Enabled Industrial Applications}, author = {Deebak, B. D. and Memon, Fida Hussain and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Wang, Weizheng and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TII.2022.3159164}, volume = {19}, pages = {243-250}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and ResultsRen Yang, Radu Timofte, Meisong Zheng, and 76 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2022
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and ResultsRen Yang, Radu Timofte, Meisong Zheng, and 76 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2022This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video. In this challenge, we proposed the LDV 2.0 dataset, which includes the LDV dataset (240 videos) and 95 additional videos. This challenge includes three tracks. Track 1 aims at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP. Track 2 and Track 3 target both the super-resolution and quality enhancement of HEVC compressed video. They require x2 and x4 super-resolution, respectively. The three tracks totally attract more than 600 registrations. In the test phase, 8 teams, 8 teams and 12 teams submitted the final results to Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of super-resolution and quality enhancement of compressed video. The proposed LDV 2.0 dataset is available at https://github.com/RenYang-home/LDV_dataset. The homepage of this challenge (including open-sourced codes) is at https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE22_VEnh_SR.
@inproceedings{NTIRE2022, title = {NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and Results}, author = {Yang, Ren and Timofte, Radu and Zheng, Meisong and Xing, Qunliang and Qiao, Minglang and Xu, Mai and Jiang, Lai and Liu, Huaida and Chen, Ying and Ben, Youcheng and Zhou, Xiao and Fu, Chen and Cheng, Pei and Yu, Gang and Li, Junyi and Wu, Renlong and Zhang, Zhilu and Shang, Wei and Lv, Zhengyao and Chen, Yunjin and Zhou, Mingcai and Ren, Dongwei and Zhang, Kai and Zuo, Wangmeng and Ostyakov, Pavel and Dmitry, Vyal and Soltanayev, Shakarim and Sergey, Chervontsev and Magauiya, Zhussip and Zou, Xueyi and Yan, Youliang and Michelini, Pablo Navarrete and Lu, Yunhua and Zhang, Diankai and Liu, Shaoli and Gao, Si and Wu, Biao and Zheng, Chengjian and Zhang, Xiaofeng and Lu, Kaidi and Wang, Ning and Canh, Thuong Nguyen and Bach, Thong and Wang, Qing and Sun, Xiaopeng and Ma, Haoyu and Zhao, Shijie and Li, Junlin and Xie, Liangbin and Shi, Shuwei and Yang, Yujiu and Wang, Xintao and Gu, Jinjin and Dong, Chao and Shi, Xiaodi and Nian, Chunmei and Jiang, Dong and Lin, Jucai and Xie, Zhihuai and Ye, Mao and Luo, Dengyan and Peng, Liuhan and Chen, Shengjie and Liu, Xin and Wang, Qian and Liu, Xin and Liang, Boyang and Dong, Hang and Huang, Yuhao and Chen, Kai and Guo, Xingbei and Sun, Yujing and Wu, Huilei and Wei, Pengxu and Huang, Yulin and Chen, Junying and Hyun Lee, Ik and Ali Khowaja, Sunder and Yoon, Jiseok}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)}, pages = {1220-1237}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00129}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 UAV-Enabled Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Networks for Ground-Air-Ground CommunicationsQunshu Wang, Xingwang Li, Surbhi Bhatia, and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2022
UAV-Enabled Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Networks for Ground-Air-Ground CommunicationsQunshu Wang, Xingwang Li, Surbhi Bhatia, and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2022Both unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) have gradually become promising technologies for the fifth generation (5G) driven green Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks on account of their unique advantages of massive connections, higher spectral efficiency and flexibility. Motivated by this, we propose a 3-hop NOMA UAV-aided green communication network framework, where UAVs serve as aerial relays to support two groups of ground users. A stochastic geometry approach is invoked to model the spatial positions of the two group users. Under the realistic assumption, imperfect successive interference cancelation (ipSIC) is considered. To evaluate the performance of the proposed framework, theoretical expressions are derived to facilitate the outage performance evaluation of the far user (FU) and the near user (NU). Moreover, the asymptotic behaviors for the outage probability (OP) of both the FU and the NU in the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regime are explored by obtaining diversity orders. Finally, the system throughputs under the delay-limited transmission mode are investigated. Numerical results confirm that: 1) For uplink transmission, there exist outage floors for the OP of both ipSIC and perfect SIC (pSIC) due to interference from the NU; 2) For downlink transmission, an outage floor exists for the OP of the NU under the condition of ipSIC; 3) For uplink NOMA/orthogonal multiple access (OMA) transmission, the outage performances of both the FU and the NU with NOMA outperform OMA in the low SNRs, while OMA has better performance in the high SNR regime; 4) For downlink NOMA/OMA, the outage performances of both the FU and the NU under pSIC outperform OMA.
@article{UAV, title = {UAV-Enabled Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Networks for Ground-Air-Ground Communications}, author = {Wang, Qunshu and Li, Xingwang and Bhatia, Surbhi and Liu, Yuanwei and Alex, Linss T. and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Menon, Varun G.}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TGCN.2022.3152601}, volume = {6}, pages = {1340-1354}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 A Lightweight Blockchain-Based Remote Mutual Authentication for AI-Empowered IoT Sustainable Computing SystemsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022
A Lightweight Blockchain-Based Remote Mutual Authentication for AI-Empowered IoT Sustainable Computing SystemsB. D. Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 4 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022Internet of Things (IoT) has led to significant advancements in communication technologies, specifically, concerning IoT-based sustainable information systems. Lately, industry-academic communities have made great strides for the development of security in IoT-based applications, such as traffic management, industrial automation systems, military surveillance systems, transportation, parking, etc. The sustainable IoT converges AI and blockchain technologies for enhancing quality of individual’s life. As a result, emerging IoT applications operate a distributed ledger technology to provide robust-level of encryption and execution for contractual agreement that resolves interoperability and security issues. Thus, this article proposes a blockchain-based remote mutual authentication (B-RMA) that considers smart devices and cloud networks to offer security and privacy. The proposed B-RMA can coexist with the IoT-based smart environment to decentralize the processing of user authentication requests. The prominence of the proposed strategies including security efficiency and privacy protection, is evaluated using informal security analysis. Moreover, a runtime platform “Node.js” was used to analyze the communication metrics, such as execution time, throughput, and overhead ratio, over the concurrent requests. The investigation results prove that the B-RMA achieves a scalable environment, accordingly.
@article{LightweightBchain, title = {A Lightweight Blockchain-Based Remote Mutual Authentication for AI-Empowered IoT Sustainable Computing Systems}, author = {Deebak, B. D. and Memon, Fida Hussain and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Wang, Weizheng and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh and Su, Chunhua}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2022.3152546}, volume = {10}, pages = {6652-6660}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 FuzzyAct: A Fuzzy-Based Framework for Temporal Activity Recognition in IoT Applications Using RNN and 3D-DWTFayaz Ali Dharejo, Muhammad Zawish, Yuanchun Zhou, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022
FuzzyAct: A Fuzzy-Based Framework for Temporal Activity Recognition in IoT Applications Using RNN and 3D-DWTFayaz Ali Dharejo, Muhammad Zawish, Yuanchun Zhou, and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022Despite massive research in deep learning, the human activity recognition (HAR) domain still suffers from key challenges in terms of accurate classification and detection. The core idea behind recognizing activities accurately is to assist Internet-of-things (IoT) enabled smart surveillance systems. Thereby, this work is based on the joint use of discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and recurrent neural network (RNN) to classify and detect human activities accurately. Recent approaches on HAR exploit the three-dimensional (3-D) convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to extract spatial information, which adds a computational burden. In our case, features are extracted using 3D-DWT instead of 3-D CNNs, performed in three steps of 1D-DWT to reflect the spatio-temporal features of human action. Given the features, the RNN produces an output label for each video clip taking care of the long-term temporal consistency among close predictions in the output sequence. It is noticed that feature extraction through 3D-DWT essentially recovers the multiple angles of an activity. Many HAR techniques distinguish an activity based on the posture of an image frame rather than learning the transitional relationship between postures in the temporal sequence, resulting in degraded accuracy. To address this problem, in this article, we designed a novel rank-based fuzzy approach that segregates activities precisely by ranking the probabilities of activities based on confidence scores. FuzzyAct achieved an average mean average precision (mAP) of 0.8012 mAP on the ActivityNet dataset, and outperformed the baseline counterparts and other state-of-the-art approaches on benchmark datasets. Finally, we present a mechanism to compress the proposed RNN for edge-enabled IoT applications.
@article{FuzzyACT, title = {FuzzyAct: A Fuzzy-Based Framework for Temporal Activity Recognition in IoT Applications Using RNN and 3D-DWT}, author = {Dharejo, Fayaz Ali and Zawish, Muhammad and Zhou, Yuanchun and Davy, Steven and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Fu, Yanjie and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3152106}, volume = {30}, pages = {4578-4592}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Seamless privacy-preservation and authentication framework for IoT-enabled smart eHealth systemsBD Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Xiaochun Cheng, and 5 more authorsSustainable Cities and Society, 2022
Seamless privacy-preservation and authentication framework for IoT-enabled smart eHealth systemsBD Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Xiaochun Cheng, and 5 more authorsSustainable Cities and Society, 2022The initiatives of sustainable urbanization use ICT-based innovation to improve service efficiencies of smart cities and to discover modern economic opportunities. The smart sustainable cities prefer a reliable IoT connectivity and data integration to meet the standard constraints of emerging computing paradigms with enabling techhnologies. The computing paradigms including cloud, fog, and edge are nowadays driving the technological advancement to enrich the features of the digital application (DApp) including interactive, intuitive, and personalized. DApp utilizes the essential characteristics of the enabling technologies such as heterogeneity, resource constraints, connectivity, and mobility to standardize the nature of smart intelligence via service agents. In the connection of massive IoT services, DApp involves continuous generation of IoT data over a dedicated gateway to offer extensive connectivity and improved access control. In the past, most of the existing mechanisms have primarily focused on security management for IoT networks to operate massive application services. However, a key issue of privacy-preserving for massive IoT is still challenging to ensure device protection. Importantly, the existing mechanisms fail to claim security efficiencies in terms of user anonymity and authentication key exchange using formal proof. Thus, this paper presents a seamless authentication framework with privacy-preserving (SAF-PP) protocol to deal with security and privacy issues of smart eHealth intelligence. The formal analysis proves that the proposed SAF-PP can adhere to significant security properties while improving the system efficiency rate. The performance analysis also shows that the proposed SAF-PP is more efficient in increasing the active users with an improved packet delivery ratio and network lifetime.
@article{SeamlessPrivacy, title = {Seamless privacy-preservation and authentication framework for IoT-enabled smart eHealth systems}, author = {Deebak, BD and Memon, Fida Hussain and Cheng, Xiaochun and Dev, Kapal and Hu, Jia and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh and Choi, Kyung Huyn}, journal = {Sustainable Cities and Society}, year = {2022}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.scs.2021.103661}, volume = {80}, pages = {103661}, dimensions = {true}, }
2021
-
 AI-enabled privacy-preservation phrase with multi-keyword ranked searching for sustainable edge-cloud networks in the era of industrial IoTBD Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsAd Hoc Networks, 2021
AI-enabled privacy-preservation phrase with multi-keyword ranked searching for sustainable edge-cloud networks in the era of industrial IoTBD Deebak, Fida Hussain Memon, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsAd Hoc Networks, 2021The integration of sensing technologies and cloud computing signifies the design perspectives of electronic healthcare systems. It has its own application domain to upload the clinical data of the patients and treatment procedures to the cloud server. Moreover, the data user may process the queries with suitable sensing parameters to obtain an appropriate medical record. As a result, the development of the Industrial Internet of Things (I-IoT) demands practical insights, trustworthiness, and reliability of intelligent automation to prevent the occurrence of potential risks in the process of production. In the past, multi-keyword searching (MKS) over encrypted cloud data has attracted researchers’ attention. As cloud computing is highly practicing, data owners may easily outsource any kind of system data to commercial sites using the Industrial Internet of Things (I-IoT). However, data privacy and protection should be ensured using encryption techniques before any sensitive data is outsourced over insecure public networks. Providing cloud data encryption and secure keyword searching still exist as challenging issues. In I-IoT, cloud computing deals with a large amount of data users and documents, thus a technique like MKS is highly necessitated to process the search request and secure query processing. Thus, this paper presents a privacy-preservation phrase with multi-keyword ranked searching (PPP-MKRS) that introduces optimized filtering, binary tree index structure, and conjunctive keyword search to achieve secure searching efficiency. The experimental analysis shows that the proposed PPP-MKRS scheme consumes less computation, storage, and verification time in comparison with other searching encryption techniques.
@article{Adhoc, title = {AI-enabled privacy-preservation phrase with multi-keyword ranked searching for sustainable edge-cloud networks in the era of industrial IoT}, author = {Deebak, BD and Memon, Fida Hussain and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Qureshi, Nawab Muhammad Faseeh}, journal = {Ad Hoc Networks}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102740}, volume = {125}, pages = {102740}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Towards soft real-time fault diagnosis for edge devices in industrial IoT using deep domain adaptation training strategyDileep Kumar, Sanaullah Mehran Ujjan, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsJournal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2021
Towards soft real-time fault diagnosis for edge devices in industrial IoT using deep domain adaptation training strategyDileep Kumar, Sanaullah Mehran Ujjan, Kapal Dev, and 3 more authorsJournal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2021Artificial intelligence and industrial internet of things (IIoT) have been rejuvenating the fault diagnosis systems in Industry 4.0 for avoiding major financial losses caused by faults in rotating machines. Meanwhile, the diagnostic systems are provided with a number of sensory inputs that introduce variations in input space which causes difficulty for the algorithms in edge devices. This issue is generally dealt with bi-view cross-domain learning approach. We propose a soft real-time fault diagnosis system for edge devices using domain adaptation training strategy. The investigation is carried out using deep learning models that can learn representations irrespective of input dimensions. A comparative analysis is performed on a publicly available dataset to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed approach which achieved accuracy of 88.08%. The experimental results show that our method using long short-term memory network achieves the best results for the bearing fault detection in an IIoT environmental setting.
@article{JPDC, title = {Towards soft real-time fault diagnosis for edge devices in industrial IoT using deep domain adaptation training strategy}, author = {Kumar, Dileep and Ujjan, Sanaullah Mehran and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Bhatti, Naveed Ahmed and Hussain, Tanweer}, journal = {Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.jpdc.2021.10.005}, volume = {160}, pages = {90-99}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Toward Energy-Efficient Distributed Federated Learning for 6G NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Parus Khowaja, and 1 more authorIEEE Wireless Communications, 2021
Toward Energy-Efficient Distributed Federated Learning for 6G NetworksSunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Parus Khowaja, and 1 more authorIEEE Wireless Communications, 2021The provision of communication services via portable and mobile devices, such as aerial base stations, is a crucial concept to be realized in 5G/6G networks. Conventionally, IoT/edge devices need to transmit data directly to the base station for training the model using machine learning techniques. The data transmission introduces privacy issues that might lead to security concerns and monetary losses. Recently, federated learning was proposed to partially solve privacy issues via model sharing with the base station. However, the centralized nature of federated learning only allows the devices within the vicinity of base stations to share trained models. Furthermore, the long-range communication compels the devices to increase transmission power, which raises energy efficiency concerns. In this work, we propose the distributed federated learning (DBFL) framework that overcomes the connectivity and energy efficiency issues for distant devices. The DBFL framework is compatible with mobile edge computing architecture that connects the devices in a distributed manner using clustering protocols. Experimental results show that the framework increases the classification performance by 7.4 percent in comparison to conventional federated learning while reducing the energy consumption.
@article{DBFL, title = {Toward Energy-Efficient Distributed Federated Learning for 6G Networks}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Parus and Bellavista, Paolo}, journal = {IEEE Wireless Communications}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MWC.012.2100153}, volume = {28}, pages = {34-40}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Flexible Data Integrity Checking With Original Data Recovery in IoT-Enabled Maritime Transportation SystemsDengzhi Liu, Yong Zhang, Weizheng Wang, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021
Flexible Data Integrity Checking With Original Data Recovery in IoT-Enabled Maritime Transportation SystemsDengzhi Liu, Yong Zhang, Weizheng Wang, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021Internet of things (IoT) has emerged as a promising technology that can be widely used in various industries to realize real-time information collection, so as to improve production efficiency and reduce running costs. By combining the technology of IoT, maritime transportation systems (MTS) can prevent vessels collision, improve the efficiency of maritime transportation and reduce the loss of revenue for ports and shipbuilders. The large amount of real-time data generated in IoT-enabled MTS can be efficiently utilized to predict the future trajectories and hotspots of vessels on the sea combined with historical data. However, the maritime traffic data in MTS cannot be effectively processed in traditional big data analysis methods, and the integrity of it needs to be checked before being used to achieve the prediction of trajectories and high-density areas of vessels. In this paper, we propose a flexible data integrity checking scheme with original data recovery in IoT-enabled MTS. In the proposed scheme, the data blocks of vessels are encoded based on the technology of erasure coding. To ensure the availability of the historical data, the existence and the integrity of the data elements stored in the cloud can be checked. Moreover, the original data blocks can be recovered efficiently if the encoded data elements have been corrupted or deleted. Security analysis demonstrates that the proposed scheme can be proved to be correct and is secure against malicious attacks. Performance analysis shows that our scheme is more efficient than the previous schemes.
@article{Flexible, title = {Flexible Data Integrity Checking With Original Data Recovery in IoT-Enabled Maritime Transportation Systems}, author = {Liu, Dengzhi and Zhang, Yong and Wang, Weizheng and Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TITS.2021.3125070}, volume = {24}, pages = {2618-2629}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 NEAT: A Resilient Deep Representational Learning for Fault Detection Using Acoustic Signals in IIoT EnvironmentMuhammad Aslam Jarwar, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021
NEAT: A Resilient Deep Representational Learning for Fault Detection Using Acoustic Signals in IIoT EnvironmentMuhammad Aslam Jarwar, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, and 2 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021Fault diagnostics involving the Internet-of-Things (IoT) sensors and edge devices is a challenging task due to their limited energy and computational capabilities. Another challenge concerning IoT sensors or devices is the incursion of noise when used in an industrial environment. The noisy samples affect the decision support system that could lead to financial and operational losses. This article proposes a noisy encoder using artificial intelligence of things (NEAT) architecture for fault diagnosis in IoT edge devices. NEAT combines autoencoders and Inception module to co-train the clean and noisy samples for solving the said problem. Experimental results on benchmark data sets reveal that the NEAT architecture is noise resilient in comparison to the existing works. Furthermore, we also show that the NEAT architecture has lightweight characteristics as it yields a lower number of parameters, weight storage, training, and testing times that support its real-life applicability in an Industrial IoT environment.
@article{NEAT, title = {NEAT: A Resilient Deep Representational Learning for Fault Detection Using Acoustic Signals in IIoT Environment}, author = {Jarwar, Muhammad Aslam and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal and Adhikari, Mainak and Hakak, Saqib}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2021.3109668}, volume = {10}, pages = {2864-2871}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Data Harmonization for Heterogeneous Datasets: A Systematic Literature ReviewGanesh Kumar, Shuib Basri, Abdullahi Abubakar Imam, and 3 more authorsApplied Sciences, 2021
Data Harmonization for Heterogeneous Datasets: A Systematic Literature ReviewGanesh Kumar, Shuib Basri, Abdullahi Abubakar Imam, and 3 more authorsApplied Sciences, 2021As data size increases drastically, its variety also increases. Investigating such heterogeneous data is one of the most challenging tasks in information management and data analytics. The heterogeneity and decentralization of data sources affect data visualization and prediction, thereby influencing analytical results accordingly. Data harmonization (DH) corresponds to a field that unifies the representation of such a disparate nature of data. Over the years, multiple solutions have been developed to minimize the heterogeneity aspects and disparity in formats of big-data types. In this study, a systematic review of the literature was conducted to assess the state-of-the-art DH techniques. This study aimed to understand the issues faced due to heterogeneity, the need for DH and the techniques that deal with substantial heterogeneous textual datasets. The process produced 1355 articles, but among them, only 70 articles were found to be relevant through inclusion and exclusion criteria methods. The result shows that the heterogeneity of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured (SSU) data can be managed by using DH and its core techniques, such as text preprocessing, Natural Language Preprocessing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL). These techniques are applied to many real-world applications centered on the information-retrieval domain. Several assessment criteria were implemented to measure the efficiency of these techniques, such as precision, recall, F-1, accuracy, and time. A detailed explanation of each research question, common techniques, and performance measures is also discussed. Lastly, we present readers with a detailed discussion of the existing work, contributions, and managerial and academic implications, along with the conclusion, limitations, and future research directions.
@article{DataHarmonization, title = {Data Harmonization for Heterogeneous Datasets: A Systematic Literature Review}, author = {Kumar, Ganesh and Basri, Shuib and Imam, Abdullahi Abubakar and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Capretz, Luiz Fernando and Balogun, Abdullateef Oluwagbemiga}, journal = {Applied Sciences}, year = {2021}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/app11178275}, volume = {11}, pages = {8275}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 VIRFIM: an AI and Internet of Medical Things-driven framework for healthcare using smart sensorsSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorNeural Computing and Applications, 2021
VIRFIM: an AI and Internet of Medical Things-driven framework for healthcare using smart sensorsSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, Kapal Dev, and 1 more authorNeural Computing and Applications, 2021After affecting the world in unexpected ways, the virus has started mutating which is evident with the insurgence of its new variants. The governments, hospitals, schools, industries, and humans, in general, are looking for a potential solution in the vaccine which will eventually be available, but its timeline for eradicating the virus is yet unknown. Several researchers have encouraged and recommended the use of good practices such as physical healthcare monitoring, immunity boosting, personal hygiene, mental healthcare, and contact tracing for slowing down the spread of the virus. In this article, we propose the use of smart sensors integrated with the Internet of Medical Things to cover the spectrum of good practices in an automated manner. We present hypothetical frameworks for each of the good practice modules and propose the VIrus Resistance Framework using the Internet of Medical Things (VIRFIM) to tie all the individual modules in a unified architecture. Furthermore, we validate the realization of VIRFIM framework with two case studies related to physical activity monitoring and stress detection services. We envision that VIRFIM would be influential in assisting people with the new normal for current and future pandemics as well as instrumental in halting the economic losses, respectively. We also provide potential challenges and their probable solutions in compliance with the proposed VIRFIM.
@article{VIRFIM, title = {VIRFIM: an AI and Internet of Medical Things-driven framework for healthcare using smart sensors}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Dev, Kapal and D'Aniello, Giuseppe}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-021-06434-4}, volume = {35}, pages = {16175-16192}, dimensions = {true}, } -
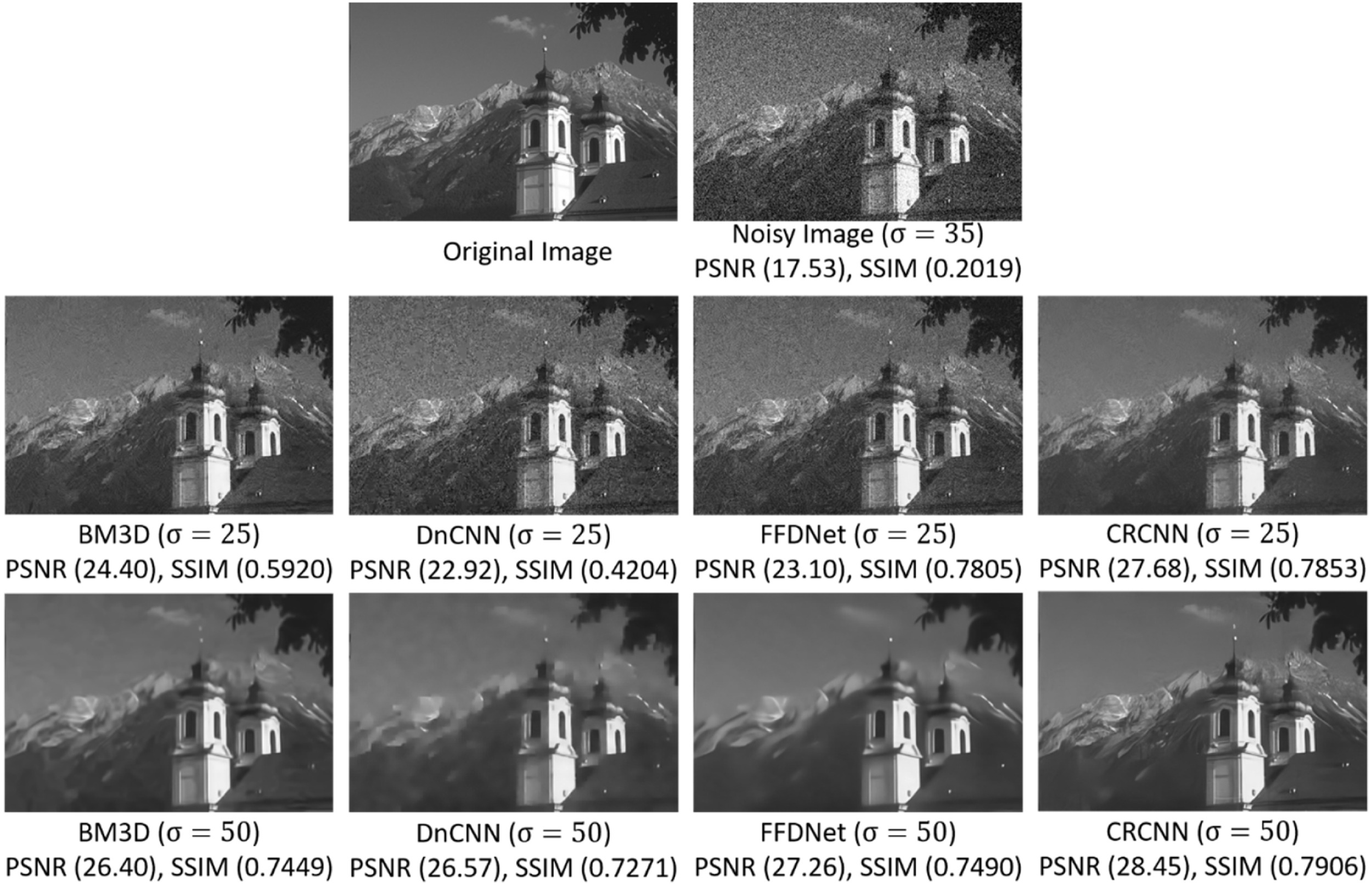 Cascaded and Recursive ConvNets (CRCNN): An effective and flexible approach for image denoisingSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeSignal Processing: Image Communication, 2021
Cascaded and Recursive ConvNets (CRCNN): An effective and flexible approach for image denoisingSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeSignal Processing: Image Communication, 2021Recently, discriminative learning methods have gained substantial interest in solving inverse imaging problems due to their decent performance and fast inferencing capability. Those methods need separate models for specific noise levels, which in turn require multiple models to be trained to denoise an image. However, images exhibit spatial variant noise which limits the applicability of such methods. In addition, the discriminative learning methods introduce artifacts such as blurring, deblocking, and so forth while denoising an image. To address these issues, we propose a cascaded and recursive convolutional neural network (CRCNN) framework which can cope with spatial variant noise and blur artifacts in a single denoising framework. The CRCNN takes into account down-sampled sub-images for fast inferencing along with the noise level map. We adopt the hybrid orthogonal projection and estimation method on the convolutional layers to improve the generalization capability of the network in terms of non-uniform and spatial variant noise levels. In contrast to the existing methods, the CRCNN framework allows both denoising and deblurring of images using a single framework which preserves the fine details in a denoised image. Extensive experiments have been conducted to validate the effectiveness and flexibility of the CRCNN framework on real as well as synthetic noisy images in comparison to the state-of-the-art denoising methods. The results show that the CRCNN performs effectively on both synthetic as well as spatial variant noise-induced images, thus, proving the practicability of the framework.
@article{CRCNN, title = {Cascaded and Recursive ConvNets (CRCNN): An effective and flexible approach for image denoising}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Signal Processing: Image Communication}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.image.2021.116420}, volume = {99}, pages = {116420}, dimensions = {true}, } -
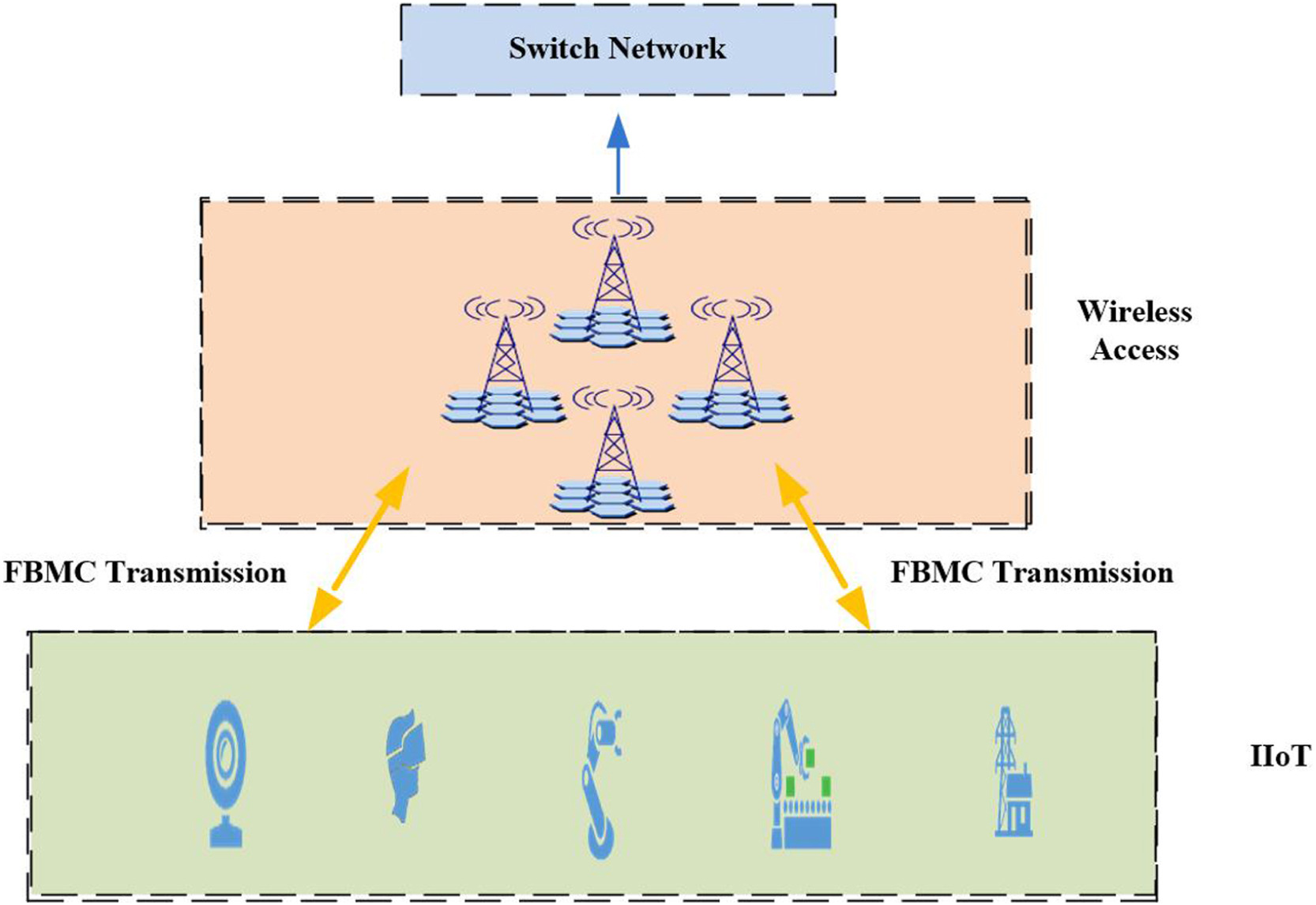 Sparse Bayesian learning based channel estimation in FBMC/OQAM industrial IoT networksHan Wang, Xingwang Li, Rutvij H. Jhaveri, and 4 more authorsComputer Communications, 2021
Sparse Bayesian learning based channel estimation in FBMC/OQAM industrial IoT networksHan Wang, Xingwang Li, Rutvij H. Jhaveri, and 4 more authorsComputer Communications, 2021The next generation of communication technology is accelerating the transformation of industrial internet of things (IIoT). Filter bank multicarrier with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (FBMC/OQAM), as a candidate wireless transmission technology for beyond fifth generation (5G), has been widely concerned by researchers. However, effective channel estimation (CE) in IIoT communication should be solved. In practice, wireless channels have block–sparse structures. For the conventional sparse channel model, the general sparse channel estimation methods do not take the potential block–sparse structure information into account. In this paper, we have investigated the sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) framework for sparse multipath CE in FBMC/OQAM communications. Block SBL (BSBL) algorithm is proposed to estimate the channel performance by exploiting the block–sparse structure of sparse multipath channel model. The BSBL method can improve the estimation performance by using the block correlation of the training matrix. Computer simulation results demonstrate the robustness of the BSBL CE approach in FBMC/OQAM systems, which can achieve lower mean square error (MSE) and bit error rate (BER) than traditional least squares (LS) method and classical compressive sensing methods. The state of art compressive sampling matching pursuit (CoSaMP) greedy algorithm with a prior knowledge of sparse degree can provide slightly better CE performance than BSBL algorithm, but the proposed method maintains robustness in practical channel scenario without the prior knowledge of sparse degree.
@article{SparseBayesian, title = {Sparse Bayesian learning based channel estimation in FBMC/OQAM industrial IoT networks}, author = {Wang, Han and Li, Xingwang and Jhaveri, Rutvij H. and Gadekallu, Thippa Reddy and Zhu, Mingfu and Ahanger, Tariq Ahamed and Khowaja, Sunder Ali}, journal = {Computer Communications}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.comcom.2021.05.020}, volume = {176}, pages = {40-45}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Adversarial Learning Networks for FinTech Applications Using Heterogeneous Data SourcesParus Khuwaja, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and Kapal DevIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021
Adversarial Learning Networks for FinTech Applications Using Heterogeneous Data SourcesParus Khuwaja, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and Kapal DevIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021The dynamic property and increasing complexity are the key challenges for modeling financial technology (FinTech)-related applications such as stock markets. Over the years, a lot of inflexible predictive strategies have been proposed for predicting stock price movements that failed to achieve satisfactory results especially when a market crash occurs. To cope with this challenge, we propose a prediction framework based on an adversarial training strategy using reinforcement learning for the said FinTech application. The framework uses a heterogeneous knowledge base, including stock prices, tweets, and global indicators. We propose a modified newton-divided difference polynomial (NDDP) for missing data imputation. The informative patterns representing the intrinsic characteristics of financial markets were extracted using long short-term memory networks (LSTM). The two adversarial networks are heterogeneous data fusion representing market crash (HDFM) Q -learning and confrontational Q -learning network. Both networks are trained in an adversarial fashion to increase the effectiveness of prediction even when the financial market is volatile. The experimental results show the importance of global indicators and the proposed adversarial learning network (ALN) for improving the predictive performance in comparison with the existing state-of-the-art works.
@article{FinTech, title = {Adversarial Learning Networks for FinTech Applications Using Heterogeneous Data Sources}, author = {Khuwaja, Parus and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2021.3100742}, volume = {10}, pages = {2194-2201}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 DDI: A Novel Architecture for Joint Active User Detection and IoT Device Identification in Grant-Free NOMA Systems for 6G and Beyond NetworksKapal Dev, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Prabhat Kumar Sharma, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021
DDI: A Novel Architecture for Joint Active User Detection and IoT Device Identification in Grant-Free NOMA Systems for 6G and Beyond NetworksKapal Dev, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Prabhat Kumar Sharma, and 3 more authorsIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021Nonorthogonal multiple access (NOMA) with a grant-free access has received a lot of attention due to its support to massive machine-type communication (mMTC) devices. The devices in grant-free systems are allowed to transmit information without undergoing an authentication process. Therefore, in such systems, the base station needs to distinguish between active and nonactive devices, called the active user detection (AUD) process. This process is challenging as the active device needs to be detected from the received signals that are superimposed. Furthermore, the identification of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices from these signals also poses a great challenge, which could help allocate resources in future generation communication systems. Motivated from the aforementioned facts, this article proposes a device detection and identification (DDI) architecture for joint AUD and IoT device identification from the received superimposed signals. The architecture extracts the Fourier patterns as the representative feature vector, which results in an improved detection and identification process. Experimental results show that the architecture not only outperforms the conventional schemes and deep neural network-based approaches in terms of success probability for the AUD task but also yields lower computational complexity. The evaluation of the DDI architecture for IoT device identification problems has also been performed and compared to various shallow learning methods to prove its efficacy.
@article{DDI, title = {DDI: A Novel Architecture for Joint Active User Detection and IoT Device Identification in Grant-Free NOMA Systems for 6G and Beyond Networks}, author = {Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Sharma, Prabhat Kumar and Chowdhry, Bhawani Shankar and Tanwar, Sudeep and Fortino, Giancarlo}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2021.3095255}, volume = {9}, pages = {2906-2917}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Triage of potential COVID-19 patients from chest X-ray images using hierarchical convolutional networksKapal Dev, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Ankur Singh Bist, and 2 more authorsNeural Computing and Applications, 2021
Triage of potential COVID-19 patients from chest X-ray images using hierarchical convolutional networksKapal Dev, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Ankur Singh Bist, and 2 more authorsNeural Computing and Applications, 2021The current COVID-19 pandemic has motivated the researchers to use artificial intelligence techniques for a potential alternative to reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction due to the limited scale of testing. The chest X-ray (CXR) is one of the alternatives to achieve fast diagnosis, but the unavailability of large-scale annotated data makes the clinical implementation of machine learning-based COVID detection difficult. Another issue is the usage of ImageNet pre-trained networks which does not extract reliable feature representations from medical images. In this paper, we propose the use of hierarchical convolutional network (HCN) architecture to naturally augment the data along with diversified features. The HCN uses the first convolution layer from COVIDNet followed by the convolutional layers from well-known pre-trained networks to extract the features. The use of the convolution layer from COVIDNet ensures the extraction of representations relevant to the CXR modality. We also propose the use of ECOC for encoding multiclass problems to binary classification for improving the recognition performance. Experimental results show that HCN architecture is capable of achieving better results in comparison with the existing studies. The proposed method can accurately triage potential COVID-19 patients through CXR images for sharing the testing load and increasing the testing capacity.
@article{Triage, title = {Triage of potential COVID-19 patients from chest X-ray images using hierarchical convolutional networks}, author = {Dev, Kapal and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Bist, Ankur Singh and Saini, Vaibhav and Bhatia, Surbhi}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-020-05641-9}, volume = {35}, pages = {23861-23876}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Q-learning and LSTM based deep active learning strategy for malware defense in industrial IoT applicationsSunder Ali Khowaja, and Parus KhuwajaMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2021
Q-learning and LSTM based deep active learning strategy for malware defense in industrial IoT applicationsSunder Ali Khowaja, and Parus KhuwajaMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2021Edge devices are extensively used as intermediaries between the device and the service layer in an industrial Internet of things (IIoT) environment. These devices are quite vulnerable to malware attacks. Existing studies have worked on designing complex learning algorithms or deep architectures to accurately classify malware assuming that a sufficient number of labeled examples are provided. In the real world, getting labeled examples is one of the major issues for training any classification algorithm. Recent advances have allowed researchers to use active learning strategies that are trained on a handful of labeled examples to perform the classification task, but they are based on the selection of informative instances. This study integrates the Q-learning characteristics into an active learning framework, which allows the network to either request or predict a label during the training process. We proposed the use of phase space embedding, sparse autoencoder, and LSTM with the action-value function to classify malware applications while using a handful of labeled examples. The network relies on its uncertainty to either request or predict a label. The experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve better accuracy than the supervised learning strategy while using few labeled requests. The results also show that the trained network is resilient to the adversarial attacks, which proves the robustness of the proposed method. Additionally, this study explores the tradeoff between classification accuracy and number of label requests via the choice of rewards and the use of decision-level fusion strategies to boost the classification performance. Furthermore, we also provide a hypothetical framework as an implication of the proposed method.
@article{Qlearning, title = {Q-learning and LSTM based deep active learning strategy for malware defense in industrial IoT applications}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus}, journal = {Multimedia Tools and Applications}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s11042-020-10371-0}, volume = {80}, pages = {14637-14663}, dimensions = {true}, }
2020
-
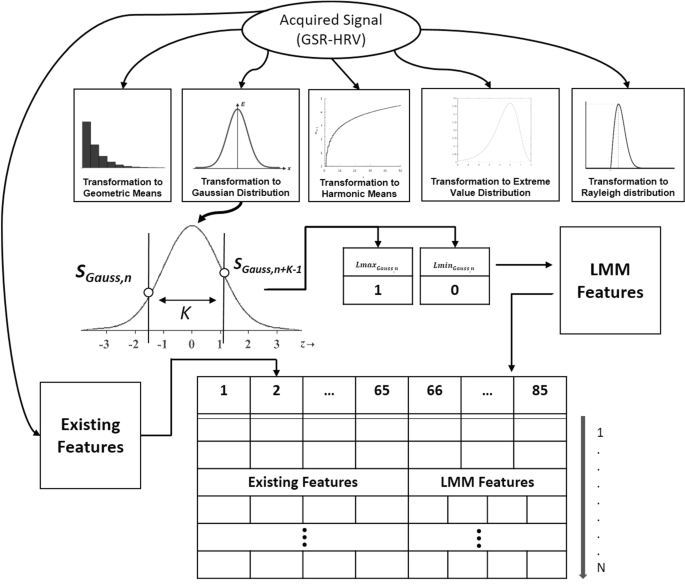 Toward soft real-time stress detection using wrist-worn devices for human workspacesSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsSoft Computing, 2020
Toward soft real-time stress detection using wrist-worn devices for human workspacesSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsSoft Computing, 2020Continuous exposure to stress leads to many health problems and substantial economic loss in companies. A lot of attention has been given to the development of wearable systems for stress monitoring to tackle its long-term effects such as confusion, high blood pressure, insomnia, depression, headache and inability to take decisions. Accurate detection of stress from physiological measurements embedded in wearable devices has been the primary goal in the healthcare industry. Advanced sensor devices with a high sampling rate have been proven to achieve high accuracy in many earlier works. However, there has been a little attempt to employ consumer-based devices with a low sampling rate, which potentially degrades the performance of detection systems. In this paper, we propose a set of new features, local maxima and minima (LMM), from heart rate variability and galvanic skin response sensors along with the voting and similarity-based fusion (VSBF) method, to improve the detection performance. The proposed feature set and fusion method are first tested on the acquired dataset which is collected using the wrist-worn devices with a low sampling rate in workplace environments and validated on a publicly available dataset, driveDB from PhysioNet. The experimental results from both datasets prove that the LMM features can improve the detection accuracy for different classifiers in general. The proposed VSBF method further boosts the recognition accuracy by 5.69% and 2.90% in comparison with the AdaBoost, which achieves the highest accuracy as a single classifier on the acquired, and the DriveDB dataset, respectively. Our analyses show that the stress detection system using the acquired dataset yields an accuracy of 92.05% and an F1 score of 0.9041. Based on the analyses, a soft real-time system is implemented and validated to prove the applicability of the proposed work for stress detection in a real environment.
@article{Stress, title = {Toward soft real-time stress detection using wrist-worn devices for human workspaces}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Prabono, Aria Ghora and Setiawan, Feri and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Soft Computing}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00500-020-05338-0}, volume = {25}, pages = {2793-2820}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 CAPHAR: context-aware personalized human activity recognition using associative learning in smart environmentsSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeHuman-centric Computing and Information Sciences, 2020
CAPHAR: context-aware personalized human activity recognition using associative learning in smart environmentsSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeHuman-centric Computing and Information Sciences, 2020The existing action recognition systems mainly focus on generalized methods to categorize human actions. However, the generalized systems cannot attain the same level of recognition performance for new users mainly due to the high variance in terms of human behavior and the way of performing actions, i.e. activity handling. The use of personalized models based on similarity was introduced to overcome the activity handling problem, but the improvement was found to be limited as the similarity was based on physiognomies rather than the behavior. Moreover, human interaction with contextual information has not been studied extensively in the domain of action recognition. Such interactions can provide an edge for both recognizing high-level activities and improving the personalization effect. In this paper, we propose the context-aware personalized human activity recognition (CAPHAR) framework which computes the class association rules between low-level actions/sensor activations and the contextual information to recognize high-level activities. The personalization in CAPHAR leverages the individual behavior process using a similarity metric to reduce the effect of the activity handling problem. The experimental results on the “daily lifelog” dataset show that CAPHAR can achieve at most 23.73% better accuracy for new users in comparison to the existing classification methods.
@article{CAPHAR, title = {CAPHAR: context-aware personalized human activity recognition using associative learning in smart environments}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1186/s13673-020-00240-y}, volume = {10}, pages = {35}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Fine-grained emotion recognition: fusion of physiological signals and facial expressions on spontaneous emotion corpusFeri Setiawan, Aria Ghora Prabono, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 5 more authorsInternational Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 2020
Fine-grained emotion recognition: fusion of physiological signals and facial expressions on spontaneous emotion corpusFeri Setiawan, Aria Ghora Prabono, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and 5 more authorsInternational Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 2020The recognition of fine-grained emotions (i.e., happiness, sad, etc.) has shown its importance in a real-world implementation. The emotion recognition using physiological signals is a challenging task due to the precision of the labelled data while using facial expressions is less appropriate for the real environment. This work proposes a framework for fusing physiological signals and facial expressions modalities to improve classification performance. The feature-level fusion (FLF) and decision-level fusion (DLF) techniques are explored in this work to recognise seven fine-grained emotions. The performance of the proposed framework is evaluated using 34 subjects’ data. Our result shows that the fusion of the multiple modalities could improve the overall accuracy compared to the unimodal system by 11.66% and 13.63% for facial expression and physiological signals, respectively. Our work achieved a 73.23% accuracy for seven emotions which is considerable accuracy for the spontaneous emotion corpus.
@article{FusionEmotion, title = {Fine-grained emotion recognition: fusion of physiological signals and facial expressions on spontaneous emotion corpus}, author = {Setiawan, Feri and Prabono, Aria Ghora and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Kim, Wangsoo and Park, Kyoungsoo and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong and Hong, Jin Pyo}, journal = {International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Inderscience}, doi = {10.1504/IJAHUC.2020.110824}, volume = {35}, pages = {162-178}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Face Recognition for Smart Door Lock System using Hierarchical NetworkMuhammad Waseem, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Ramesh Kumar Ayyasamy, and 1 more authorIn 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI), 2020
Face Recognition for Smart Door Lock System using Hierarchical NetworkMuhammad Waseem, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Ramesh Kumar Ayyasamy, and 1 more authorIn 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI), 2020Face recognition system is broadly used for human identification because of its capacity to measure the facial points and recognize the identity in an unobtrusive way. The application of face recognition systems can be applied to surveillance at home, workplaces, and campuses, accordingly. The problem with existing face recognition systems is that they either rely on the facial key points and landmarks or the face embeddings from FaceNet for the recognition process. In this paper, we propose a hierarchical network (HN) framework which uses pre-trained architecture for recognizing faces followed by the validation from face embeddings using FaceNet. We also designed a real-time face recognition security door lock system connected with raspberry pi as an implication of the proposed method. The evaluation of the proposed work has been conducted on the dataset collected from 12 students from Faculty of Engineering and Technology, University of Sindh. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better results over existing works. We also carried out a comparison on random faces acquired from the Internet to perform face recognition and results shows that the proposed HN framework is resilient to the randomly acquired faces.
@inproceedings{Facelook, title = {Face Recognition for Smart Door Lock System using Hierarchical Network}, author = {Waseem, Muhammad and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Ayyasamy, Ramesh Kumar and Bashir, Farhan}, booktitle = {2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI)}, pages = {51-56}, year = {2020}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ICCI51257.2020.9247836}, dimensions = {true}, }
2019
-
 Hybrid and hierarchical fusion networks: a deep cross-modal learning architecture for action recognitionSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeNeural Computing and Applications, 2019
Hybrid and hierarchical fusion networks: a deep cross-modal learning architecture for action recognitionSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeNeural Computing and Applications, 2019Two-stream networks have provided an alternate way of exploiting the spatiotemporal information for action recognition problem. Nevertheless, most of the two-stream variants perform the fusion of homogeneous modalities which cannot efficiently capture the action-motion dynamics from the videos. Moreover, the existing studies cannot extend the streams beyond the number of modalities. To address these limitations, we propose a hybrid and hierarchical fusion (HHF) networks. The hybrid fusion handles non-homogeneous modalities and introduces a cross-modal learning stream for effective modeling of motion dynamics while extending the networks from existing two-stream variants to three and six streams. On the other hand, the hierarchical fusion makes the modalities consistent by modeling long-term temporal information along with the combination of multiple streams to improve the recognition performance. The proposed network architecture comprises of three fusion tiers: the hybrid fusion itself, the long-term fusion pooling layer which models the long-term dynamics from RGB and optical flow modalities, and the adaptive weighting scheme for combining the classification scores from several streams. We show that the hybrid fusion has different representations from the base modalities for training the cross-modal learning stream. We have conducted extensive experiments and shown that the proposed six-stream HHF network outperforms the existing two- and four-stream networks, achieving the state-of-the-art recognition performance, 97.2% and 76.7% accuracies on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets, respectively, which are widely used in action recognition studies.
@article{HybridFusion, title = {Hybrid and hierarchical fusion networks: a deep cross-modal learning architecture for action recognition}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-019-04578-y}, volume = {32}, pages = {10423-10434}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Semantic Image Networks for Human Action RecognitionSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeInternational Journal of Computer Vision, 2019
Semantic Image Networks for Human Action RecognitionSunder Ali Khowaja, and Seok-Lyong LeeInternational Journal of Computer Vision, 2019In this paper, we propose the use of a semantic image, an improved representation for video analysis, principally in combination with Inception networks. The semantic image is obtained by applying localized sparse segmentation using global clustering prior to the approximate rank pooling, which summarizes the motion characteristics in single or multiple images. It incorporates the background information by overlaying a static background from the window onto the subsequent segmented frames. The idea is to improve the action–motion dynamics by focusing on the region, which is important for action recognition and encoding the temporal variances using the frame ranking method. We also propose the sequential combination of Inception-ResNetv2 and long–short-term memory network (LSTM) to leverage the temporal variances for improved recognition performance. Extensive analysis has been carried out on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets, which are widely used in action recognition studies. We show that (1) the semantic image generates better activations and converges faster than its original variant, (2) using segmentation prior to approximate rank pooling yields better recognition performance, (3) the use of LSTM leverages the temporal variance information from approximate rank pooling to model the action behavior better than the base network, (4) the proposed representations are adaptive as they can be used with existing methods such as temporal segment and I3D ImageNet + Kinetics network to improve the recognition performance, and (5) the four-stream network architecture pre-trained on ImageNet + Kinetics and fine-tuned using the proposed representation achieves the state-of-the-art performance, 99.1% and 83.7% recognition accuracy on UCF101 and HMDB51, respectively.
@article{SINet, title = {Semantic Image Networks for Human Action Recognition}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s11263-019-01248-3}, volume = {128}, pages = {393-419}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Prediction of stock movement using phase space reconstruction and extreme learning machinesParus Khuwaja, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Imamuddin Khoso, and 1 more authorJournal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 2019
Prediction of stock movement using phase space reconstruction and extreme learning machinesParus Khuwaja, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Imamuddin Khoso, and 1 more authorJournal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 2019Stock movement prediction is regarded as one of the most difficult, meaningful, and attractive research issues in the field of financial markets. The stock price data have non-stationary, noisy, and non-linear characteristics which make the movement and its prediction a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a framework to predict the stock price movement using phase space reconstruction (PSR) and extreme learning machines (ELM). The uniqueness of the framework is reflected by its feature transformation technique which computes the information distance from the transformed features in phase space. The distance from phase space dimensions are modelled with ELM to predict the stock price movement. A decision-level fusion is performed on the ELM models trained using each category of features to improve the prediction performance. The framework has been validated on one of the challenging Borsa Istanbul (BIST 100) dataset which is a widely used dataset in stock price prediction studies. The results from the proposed framework are compared with the conventional machine learning pipeline as well as the baseline methods, i.e., random and Naïve approach to show the effectiveness in prediction performance. Experimental results reveal that the framework improves predictive performance by 4.5% in terms of F-measure values.
@article{ELM, title = {Prediction of stock movement using phase space reconstruction and extreme learning machines}, author = {Khuwaja, Parus and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khoso, Imamuddin and Lashari, Intizar Ali}, journal = {Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Taylor and Francis}, doi = {10.1080/0952813X.2019.1620870}, volume = {32}, pages = {59-79}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 A framework for retinal vessel segmentation from fundus images using hybrid feature set and hierarchical classificationSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, and Imdad Ali IsmailiSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2019
A framework for retinal vessel segmentation from fundus images using hybrid feature set and hierarchical classificationSunder Ali Khowaja, Parus Khuwaja, and Imdad Ali IsmailiSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2019Retinal blood vessels play an imperative role in detection of many ailments, such as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and diabetic retinopathy. The automated way of segmenting vessels from retinal images can help in early detection of many diseases. In this paper, we propose a framework based on hybrid feature set and hierarchical classification approach to segment blood vessels from digital retinal images. Firstly, we apply bidirectional histogram equalization on the inverted green channel to enhance the fundus image. Six discriminative feature extraction methods have been employed comprising of local intensities, local binary patterns, histogram of gradients, divergence of vector field, high-order local autocorrelations, and morphological transformation. The selection of feature sets has been carried out by classifying vessel and background pixels using random forests and evaluating the segmentation performance for each category of features. The selected feature sets are then used in conjunction with our proposed hierarchical classification approach to segment the vessels. The proposed framework has been tested on the DRIVE, STARE, and CHASEDB1 which are the benchmark datasets for retinal vessel segmentation methods. The results obtained from the experimental analysis show that the proposed framework can achieve better results than most state-of-the-art methods.
@article{Retinal, title = {A framework for retinal vessel segmentation from fundus images using hybrid feature set and hierarchical classification}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Khuwaja, Parus and Ismaili, Imdad Ali}, journal = {Signal, Image and Video Processing}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s11760-018-1366-x}, volume = {13}, pages = {379-387}, dimensions = {true}, }
2018
-
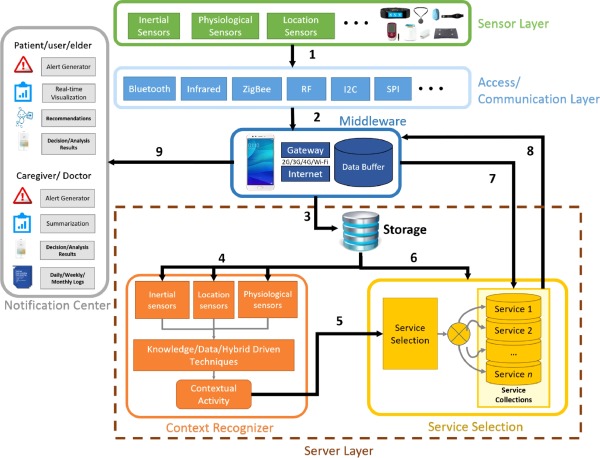 Contextual activity based Healthcare Internet of Things, Services, and People (HIoTSP): An architectural framework for healthcare monitoring using wearable sensorsSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsComputer Networks, 2018
Contextual activity based Healthcare Internet of Things, Services, and People (HIoTSP): An architectural framework for healthcare monitoring using wearable sensorsSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsComputer Networks, 2018Healthcare industry is gaining a lot of attention due to its technological advancement and the miniaturization in the form of wearable sensors. IoT-driven healthcare industry has mainly focused on the integration of sensors rather than the integration of services and people. Nonetheless, the framework for IoT-driven healthcare applications are significantly lacking. In addition, the use of semantics for ontological reasoning and the integration of mobile applications into a single framework have also been ignored in many existing studies. This work presents the implementation of Healthcare Internet of Things, Services, and People (HIoTSP) framework using wearable sensor technology. It is designed to achieve the low-cost (consumer devices), the easiness to use (interface), and the pervasiveness (wearable sensors) for healthcare monitoring along with the integration of services and agents like doctors or caregivers. The proposed framework provides the functionalities for data acquisition from wearable sensors, contextual activity recognition, automatic selection of services and applications, user interface, and value-added services such as alert generation, recommendations, and visualization. We used the publicly available dataset, PAMAP2 which is a physical activity monitoring dataset, for deriving the contextual activity. Fall and stress detection services are implemented as case studies for validating the realization of the proposed framework. Experimental analysis shows that we achieve, 87.16% accuracy for low-level contextual activities and 84.06%–86.36% for high-level contextual activities, respectively. We also achieved 91.68% and 82.93% accuracies for fall and stress detection services, respectively. The result is quite satisfactory, considering that all these services have been implemented using pervasive devices with the low-sampling rate. The real-time applicability of the proposed framework is validated by performing the response time analysis for both the services. We also provide suggestions to cope with the scalability and security issues using the HIoTSP framework and we intend to implement those suggestions in our future work.
@article{HIoTSP, title = {Contextual activity based Healthcare Internet of Things, Services, and People (HIoTSP): An architectural framework for healthcare monitoring using wearable sensors}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Prabono, Aria Ghora and Setiawan, Feri and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Computer Networks}, year = {2018}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.comnet.2018.09.003}, volume = {145}, pages = {190-206}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 A Framework for Real Time Emotion Recognition Based on Human ANS Using Pervasive DeviceFeri Setiawan, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, and 2 more authorsIn 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), 2018
A Framework for Real Time Emotion Recognition Based on Human ANS Using Pervasive DeviceFeri Setiawan, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, and 2 more authorsIn 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), 2018The concept of connected things by involving emotional aspects has been raised as a new research issue which is known as "emotional IoT". The deeper interaction between object and human shows an importance to develop a system with either cognitive or affective capabilities such as emotion. While the existing works on real time emotion recognition mostly rely on facial data, there are a few works dealing with real time emotion recognition based on physiological data using pervasive devices. In this work, we propose a framework to recognize emotion based on human physiological signals using the pervasive wearable device. This framework opposed most of the works which employed sensors which are expensive and complex in arrangement. The challenge on using pervasive devices is the low accuracy due to the low sampling rate. The approach is implemented in an end-to-end soft real time emotion recognition system using smartphone and smartwatch devices. The performance of our system was evaluated under a common environment and proved the system applicability throughout everyday life.
@inproceedings{COMPSAC, title = {A Framework for Real Time Emotion Recognition Based on Human ANS Using Pervasive Device}, author = {Setiawan, Feri and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Prabono, Aria Ghora and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, booktitle = {2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC)}, pages = {805-806}, year = {2018}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/COMPSAC.2018.00129}, dimensions = {true}, }
2017
-
 Hierarchical classification method based on selective learning of slacked hierarchy for activity recognition systemsSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeComputer Networks, 2017
Hierarchical classification method based on selective learning of slacked hierarchy for activity recognition systemsSunder Ali Khowaja, Bernardo Nugroho Yahya, and Seok-Lyong LeeComputer Networks, 2017Physical activity recognition using wearable sensors has gained significant interest from researchers working in the field of ambient intelligence and human behavior analysis. The problem of multi-class classification is an important issue in the applications which naturally has more than two classes. A well-known strategy to convert a multi-class classification problem into binary sub-problems is the error-correcting output coding (ECOC) method. Since existing methods use a single classifier with ECOC without considering the dependency among multiple classifiers, it often fails to generalize the performance and parameters in a real-life application, where different numbers of devices, sensors and sampling rates are used. To address this problem, we propose a unique hierarchical classification model based on the combination of two base binary classifiers using selective learning of slacked hierarchy and integrating the training of binary classifiers into a unified objective function. Our method maps the multi-class classification problem to multi-level classification. A multi-tier voting scheme has been introduced to provide a final classification label at each level of the solicited model. The proposed method is evaluated on two publicly available datasets and compared with independent base classifiers. Furthermore, it has also been tested on real-life sensor readings for 3 different subjects to recognize four activities i.e. Walking, Standing, Jogging and Sitting. The presented method uses same hierarchical levels and parameters to achieve better performance on all three datasets having different number of devices, sensors and sampling rates. The average accuracies on publicly available dataset and real-life sensor readings were recorded to be 95% and 85%, respectively. The experimental results validate the effectiveness and generality of the proposed method in terms of performance and parameters.
@article{ECOC, title = {Hierarchical classification method based on selective learning of slacked hierarchy for activity recognition systems}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {Computer Networks}, year = {2017}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.eswa.2017.06.040}, volume = {88}, pages = {165-177}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Energy efficient mobile user tracking system with node activation mechanism using wireless sensor networksRizwan Ali Shah, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Bhawani Shankar Chowdhary, and 1 more authorIn 2017 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital Systems (C-CODE), 2017
Energy efficient mobile user tracking system with node activation mechanism using wireless sensor networksRizwan Ali Shah, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Bhawani Shankar Chowdhary, and 1 more authorIn 2017 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital Systems (C-CODE), 2017User localization in wireless sensor networks have been given a great attention in recent times and also considered to be one of the promising applications. Many approaches for the same have been proposed based on range based and range free mechanisms for localizing the user. Similarly, tracking the user in a sensor field has also been given equal importance in association with localization. Techniques employing both these methods are mostly based on static anchor nodes or scheduling system which compromises on the lifetime of wireless sensor network. Considering the constraint of network lifetime this paper proposes localizing and tracking method with an activation scheme for tracking the mobile node efficiently while increasing the network lifetime. The system has been tested on two scenarios suggesting that the proposed method can provide the flexibility to the system which could be adjusted with reference to the user requirements. The first scenario suggests that all the nodes are activated only when the mobile user enters but as the user is localized all the nodes will get deactivated except the concerned nodes. The second scenario suggests that a predefined deployment strategy is provided with only 10% of activated nodes. The experimental results show that the proposed system achieves a better trade-off in terms of accuracy and computational complexity for single mobile node tracking.
@inproceedings{CCODE, title = {Energy efficient mobile user tracking system with node activation mechanism using wireless sensor networks}, author = {Shah, Rizwan Ali and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Chowdhary, Bhawani Shankar and Shah, Sonia}, booktitle = {2017 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital Systems (C-CODE)}, pages = {80-85}, year = {2017}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/C-CODE.2017.7918906}, dimensions = {true}, }
2016
-
 AN EFFECTIVE THRESHOLD BASED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR FALL DETECTION USING SMART DEVICESSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Industrial Engineering: Theory, Applications and Practice, 2016
AN EFFECTIVE THRESHOLD BASED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR FALL DETECTION USING SMART DEVICESSunder Ali Khowaja, Aria Ghora Prabono, Feri Setiawan, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Industrial Engineering: Theory, Applications and Practice, 2016Falls can be considered as most critical events for human workers in real world scenarios which require timely response from the emergency team. Although many have come up with fall detection devices, complex sensors arrangement and response time remain as the challenges on automatic detection, particularly in industrial environment. This paper proposes an effective fall detection algorithm using threshold based measurement approach that consists of two stages. The first focuses on optimizing the thresholds from the wearable sensor data and is required to run only one time for a specific device. The second proposes fall detection algorithms using inertial units and orientation sensor from smart devices to detect the fall. The proposed algorithms in this study take into account accelerometer and gyroscope sensors for fall detection and an orientation sensor to validate the detected fall. The wearable sensors used in this study are very common and thus does not require any special arrangement to wear them. 30% of the fall simulation data was used to acquire the optimized thresholds whereas 70% of it was used for testing of the proposed algorithm with optimized thresholds. The experiment results show better trade-off in terms of sensitivity, specificity and detection time, in comparison to the existing studies. This study also provides experimental study of fall detection algorithm by changing the placement of sensors to three different locations. It indicates the efficacy of the proposed algorithm and can adapt to changes of smart devices.
@article{FallDetect, title = {AN EFFECTIVE THRESHOLD BASED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR FALL DETECTION USING SMART DEVICES}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Prabono, Aria Ghora and Setiawan, Feri and Yahya, Bernardo Nugroho and Lee, Seok-Lyong}, journal = {International Journal of Industrial Engineering: Theory, Applications and Practice}, year = {2016}, doi = {10.23055/ijietap.2016.23.5.3300}, volume = {23}, pages = {332}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Supervised method for blood vessel segmentation from coronary angiogram images using 7-D feature vectorSunder Ali Khowaja, Mukhtiar Ali Unar, Imdad Ali Ismaili, and 1 more authorThe Imaging Science Journal, 2016
Supervised method for blood vessel segmentation from coronary angiogram images using 7-D feature vectorSunder Ali Khowaja, Mukhtiar Ali Unar, Imdad Ali Ismaili, and 1 more authorThe Imaging Science Journal, 2016With the recent advancement in medical image processing field and sophisticated simulation tools it has been possible to acquire useful information from raw images for different parts of the body. Coronary artery segmentation is the fundamental component which extract significant features from angiogram images. Cardiac catheterization is an invasive diagnostic procedure that provides important information about the structure and function of heart. The procedure usually involves X-ray images of heart, arteries using coronary angiography. The resultant images (coronary angiogram) are considered as best of way to diagnose cardiac heart disease. The main focus of coronary angiography is to find the blockage in major blood vessels, however if the blockage is not found in large blood vessels and patient persists to have pain (angina) then it is concluded that the patient is having micro vascular disease (MVD). MVD is caused by blockage or narrowing of small blood vessels in heart, unfortunately there is no specific test to diagnose MVD but it is common in people having diabetes and blood pressure. This paper proposes an automated method of vessel segmentation from coronary angiogram images using radial basis function and moment invariant-based features to extract the small blood vessel for diagnosis of MVD. Experimental results show that the proposed method is capable of extracting small blood vessels from coronary artery and can be a basis to identify key characteristics for MVD. The dataset of angiogram images have been provided by ISRA University Hospital and MATLAB is used for implementing the proposed method.
@article{vessel, title = {Supervised method for blood vessel segmentation from coronary angiogram images using 7-D feature vector}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Unar, Mukhtiar Ali and Ismaili, Imdad Ali and Khuwaja, Parus}, journal = {The Imaging Science Journal}, year = {2016}, doi = {10.1080/13682199.2016.1159815}, volume = {64}, pages = {196-203}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Facial expression recognition using two-tier classification and its application to smart home automation systemSunder Ali Khowaja, Kamran Dahri, Muhammad Aslam Kumbhar, and 1 more authorIn 2015 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), 2016
Facial expression recognition using two-tier classification and its application to smart home automation systemSunder Ali Khowaja, Kamran Dahri, Muhammad Aslam Kumbhar, and 1 more authorIn 2015 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), 2016With the convergence of smart technologies and advancement in electronic equipment the concept of smart home system swiftly escalates. The idea is to automate the home appliances according to the user requirements without human intervention. After a long tiring day and heavy workloads user will not be in a state of taking out its mobile phone and pressing the buttons for controlling home appliances. Several methods have been proposed in the design of such systems using sensors, biometrics and face detection. This paper proposes a method for detecting human emotions by taking into account the complete facial analysis, suggesting that the emotions can accurately be determined by analyzing eyes, nose and lips separately hence covering a wide range of emotions. The classification is carried out by acquiring the image of user followed by the face detection and segmenting the region of interests (ROI) i.e. eyes, nose and lips for further analysis of emotions. Principle Component Analysis (PCA) along with feature extraction techniques and Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are used for classification of emotion for the said automation system. Policies have been implemented in Java to simulate the home automation environment for testing and validation. At the instant this system has been tested on a single user with 4 basic emotions i.e. sad, anger, happiness and neutral, but this study can be a basis to develop an automated system with variety of emotions for multiple users.
@inproceedings{ICET, title = {Facial expression recognition using two-tier classification and its application to smart home automation system}, author = {Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dahri, Kamran and Kumbhar, Muhammad Aslam and Soomro, Altaf Mazhar}, booktitle = {2015 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET)}, pages = {1-6}, year = {2016}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ICET.2015.7389223}, dimensions = {true}, }